Rational design and characterization of a Rac GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor
- PMID: 15128949
- PMCID: PMC419655
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307512101
Rational design and characterization of a Rac GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor
Abstract
The signaling pathways mediated by Rho family GTPases have been implicated in many aspects of cell biology. The specificity of the pathways is achieved in part by the selective interaction between Dbl family guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and their Rho GTPase substrates. Here, we report a first-generation small-molecule inhibitor of Rac GTPase targeting Rac activation by GEF. The chemical compound NSC23766 was identified by a structure-based virtual screening of compounds that fit into a surface groove of Rac1 known to be critical for GEF specification. In vitro it could effectively inhibit Rac1 binding and activation by the Rac-specific GEF Trio or Tiam1 in a dose-dependent manner without interfering with the closely related Cdc42 or RhoA binding or activation by their respective GEFs or with Rac1 interaction with BcrGAP or effector PAK1. In cells, it potently blocked serum or platelet-derived growth factor-induced Rac1 activation and lamellipodia formation without affecting the activity of endogenous Cdc42 or RhoA. Moreover, this compound reduced Trio or Tiam1 but not Vav, Lbc, Intersectin, or a constitutively active Rac1 mutant-stimulated cell growth and suppressed Trio, Tiam1, or Ras-induced cell transformation. When applied to human prostate cancer PC-3 cells, it was able to inhibit the proliferation, anchorage-independent growth and invasion phenotypes that require the endogenous Rac1 activity. Thus, NSC23766 constitutes a Rac-specific small-molecule inhibitor that could be useful to study the role of Rac in various cellular functions and to reverse tumor cell phenotypes associated with Rac deregulation.
Figures
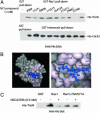


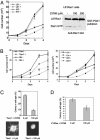
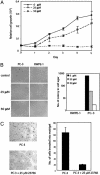
Similar articles
-
Neuronal apoptosis induced by selective inhibition of Rac GTPase versus global suppression of Rho family GTPases is mediated by alterations in distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9363-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.575217. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25666619 Free PMC article.
-
Rational design and applications of a Rac GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor.Methods Enzymol. 2006;406:554-65. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)06043-5. Methods Enzymol. 2006. PMID: 16472687
-
Mechanisms of guanine nucleotide exchange and Rac-mediated signaling revealed by a dominant negative trio mutant.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 30;279(5):3777-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308282200. Epub 2003 Nov 3. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14597635
-
Structure-function based design of small molecule inhibitors targeting Rho family GTPases.Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(11):1109-16. doi: 10.2174/156802606777812095. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16842149 Review.
-
Development of EHop-016: a small molecule inhibitor of Rac.Enzymes. 2013;33 Pt A(Pt A):117-46. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416749-0.00006-3. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Enzymes. 2013. PMID: 25033803 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of prostate smooth muscle contraction and prostate stromal cell growth by the inhibitors of Rac, NSC23766 and EHT1864.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;172(11):2905-17. doi: 10.1111/bph.13099. Epub 2015 May 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25631101 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1 and Cdc42 GTPases regulate shear stress-driven β-catenin signaling in osteoblasts.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Apr 19;433(4):502-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.03.020. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23524265 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of RhoA Exacerbates, Rather Than Dampens, Oncogenic K-Ras Induced Lung Adenoma Formation in Mice.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 1;10(6):e0127923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127923. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26030593 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal apoptosis induced by selective inhibition of Rac GTPase versus global suppression of Rho family GTPases is mediated by alterations in distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 10;290(15):9363-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.575217. Epub 2015 Feb 9. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25666619 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage motility is driven by frontal-towing with a force magnitude dependent on substrate stiffness.Integr Biol (Camb). 2015 Apr;7(4):447-53. doi: 10.1039/c4ib00260a. Integr Biol (Camb). 2015. PMID: 25768202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Etienne-Manneville, S. & Hall, A. (2002) Nature 420, 629-635. - PubMed
-
- Zheng, Y. (2001) Trends Biochem. Sci. 26, 724-732. - PubMed
-
- Zohn, I. M., Campbell, S. L., Khosravi-Far, R., Rossman, K. L. & Der, C. J. (1998) Oncogene 17, 1415-1438. - PubMed
-
- Van Aelst, L. & D'Souza-Schorey, C. (1997) Genes Dev. 11, 2295-2322. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz, A. A., Govek, E. E., Bottner, B. & Van Aelst, L. (2000) Exp. Cell Res. 261, 1-12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

