Branching sites and morphological abnormalities behave as ectopic poles in shape-defective Escherichia coli
- PMID: 15130123
- PMCID: PMC3097518
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04050.x
Branching sites and morphological abnormalities behave as ectopic poles in shape-defective Escherichia coli
Abstract
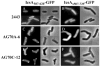
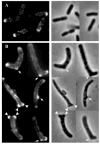
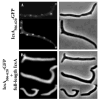
Certain mutants in Escherichia coli lacking multiple penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) produce misshapen cells containing kinks, bends and branches. These deformed regions exhibit two structural characteristics of normal cell poles: the peptidoglycan is inert to dilution by new synthesis or turnover, and a similarly stable patch of outer membrane caps the sites. To test the premise that these aberrant sites represent biochemically functional but misplaced cell poles, we assessed the intracellular distribution of proteins that localize specifically to bacterial poles. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) hybrids containing polar localization sequences from the Shigella flexneri IcsA protein or from the Vibrio cholerae EpsM protein formed foci at the poles of wild-type E. coli and at the poles and morphological abnormalities in PBP mutants. In addition, secreted wild-type IcsA localized to the outer membrane overlying these aberrant domains. We conclude that the morphologically deformed sites in these mutants represent fully functional poles or pole fragments. The results suggest that prokaryotic morphology is driven, at least in part, by the controlled placement of polar material, and that one or more of the low-molecular-weight PBPs participate in this process. Such mutants may help to unravel how particular proteins are targeted to bacterial poles, thereby creating important biochemical and functional asymmetries.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural determinants required to target penicillin-binding protein 3 to the septum of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2004 Sep;186(18):6110-7. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.18.6110-6117.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15342580 Free PMC article.
-
Branching of Escherichia coli cells arises from multiple sites of inert peptidoglycan.J Bacteriol. 2003 Feb;185(4):1147-52. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.4.1147-1152.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12562782 Free PMC article.
-
Penicillin binding protein 5 affects cell diameter, contour, and morphology of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2000 Mar;182(6):1714-21. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.6.1714-1721.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10692378 Free PMC article.
-
Approaching the physiological functions of penicillin-binding proteins in Escherichia coli.Biochimie. 2001 Jan;83(1):99-102. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(00)01205-0. Biochimie. 2001. PMID: 11254981 Review.
-
Bacterial shape.Mol Microbiol. 2003 Aug;49(3):571-80. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03607.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12914007 Review.
Cited by
-
Presence of multiple sites containing polar material in spherical Escherichia coli cells that lack MreB.J Bacteriol. 2005 Sep;187(17):6187-96. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.17.6187-6196.2005. J Bacteriol. 2005. PMID: 16109960 Free PMC article.
-
Sculpting the bacterial cell.Curr Biol. 2009 Sep 15;19(17):R812-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.033. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19906583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genome-scale proteomic screen identifies a role for DnaK in chaperoning of polar autotransporters in Shigella.J Bacteriol. 2009 Oct;191(20):6300-11. doi: 10.1128/JB.00833-09. Epub 2009 Aug 14. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19684128 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial cell wall synthesis: new insights from localization studies.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005 Dec;69(4):585-607. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.69.4.585-607.2005. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16339737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteriophage infection is targeted to cellular poles.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Jun;68(5):1107-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06205.x. Epub 2008 Mar 19. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18363799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama Y, Ito K. SecY protein, a membrane-embedded secretion factor of E. coli, is cleaved by the ompT protease in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;167:711–715. - PubMed
-
- Alley MR, Maddock JR, Shapiro L. Polar localization of a bacterial chemoreceptor. Genes Dev. 1992;6:825–836. - PubMed
-
- Autret S, Errington J. A role for division-site-selection protein MinD in regulation of internucleoid jumping of Soj (ParA) protein in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 2003;47:159–169. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Yehuda S, Rudner DZ, Losick R. RacA, a bacterial protein that anchors chromosomes to the cell poles. Science. 2003;299:532–536. - PubMed
-
- Boyd JM. Localization of the histidine kinase PilS to the poles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and identification of a localization domain. Mol Microbiol. 2000;36:153–162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

