Consensus sequence Zen
Abstract
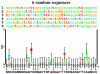
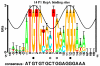
Consensus sequences are widely used in molecular biology but they have many flaws. As a result, binding sites of proteins and other molecules are missed during studies of genetic sequences and important biological effects cannot be seen. Information theory provides a mathematically robust way to avoid consensus sequences. Instead of using consensus sequences, sequence conservation can be quantitatively presented in bits of information by using sequence logo graphics to represent the average of a set of sites, and sequence walker graphics to represent individual sites.
Figures


References
-
- Abeles AL. P1 plasmid replication. Purification and DNA-binding activity of the replication protein RepA. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:3548–3555. - PubMed
-
- Barrett M, Donoghue MJ, Sober E. Against Consensus. Syst. Zool. 1991;40:486–493.
-
- Barrett M, Donoghue MJ, Sober E. Crusade? A Reply to Nelson. Syst. Biol. 1993;42:216–217.
-
- Basharin GP. On a statistical estimate for the entropy of a sequence of independent random variables. Theory Probability Appl. 1959;4(3):333–336.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
