Limited role for CXC chemokines in the pathogenesis of alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced liver injury
- PMID: 15130876
- PMCID: PMC3622103
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00300.2003
Limited role for CXC chemokines in the pathogenesis of alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced liver injury
Abstract
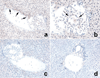
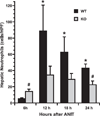
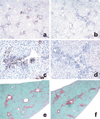
Alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate (ANIT) is a hepatotoxin that causes severe neutrophilic inflammation around portal tracts and bile ducts. The chemotactic signals that provoke this inflammatory response are unknown. In this study, we addressed the possibility that ANIT upregulates CXC chemokines in the liver and that these compounds mediate hepatic inflammation and tissue injury after ANIT treatment. Mice treated with a single dose of ANIT (50 mg/kg) exhibited rapid hepatic induction of the CXC chemokine macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2). MIP-2 derived primarily from hepatocytes, with no apparent contribution by biliary cells. In ANIT-treated mice, the induction of MIP-2 coincided with an influx of neutrophils to portal zones; this hepatic neutrophil recruitment was suppressed by 50% in mice that lack the receptor for MIP-2 (CXCR2(-/-)). Interestingly, despite their markedly reduced degree of hepatic inflammation, CXCR2(-/-) mice displayed just as much hepatocellular injury and cholestasis after ANIT treatment as wild-type mice. Moreover, after long-term exposure, ANIT CXCR2(-/-) mice developed liver fibrosis that was indistinguishable from that in wild-type mice. In summary, our data show that CXC chemokines are responsible for some of the hepatic inflammation that occurs in response to ANIT but that these compounds are not essential to the pathogenesis of either acute or chronic ANIT hepatotoxicity.
Figures



References
-
- Baggiolini M. Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature. 1998;392:565–568. - PubMed
-
- Bailie MB, Dahm LJ, Peters-Golden M, Harris RR, Carter GW, Roth RA. Leukotrienes and α-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced liver injury. Toxicology. 1995;100:139–149. - PubMed
-
- Bailie MB, Pearson JM, Fink GD, Roth RA. Platelet activating factor receptor blockade alone or in combination with leukotriene synthesis inhibition does not ameliorate α-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Lett. 1996;84:89–95. - PubMed
-
- Bautista AP. Impact of alcohol on the ability of Kupffer cells to produce chemokines and its role in alcoholic liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;15:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Bautista AP. Chronic alcohol intoxication primes Kupffer cells and endothelial cells for enhanced CC-chemokine production and concomitantly suppresses phagocytosis and chemotaxis. Front Biosci. 2002;7:117–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

