Evaluation of advanced reverse transcription-PCR assays and an alternative PCR target region for detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus
- PMID: 15131168
- PMCID: PMC404639
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.5.2043-2047.2004
Evaluation of advanced reverse transcription-PCR assays and an alternative PCR target region for detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus
Abstract
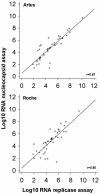
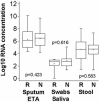
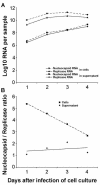
First-generation reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) assays for severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) gave false-negative results in a considerable fraction of patients. In the present study, we evaluated two second-generation, replicase (R) gene-based, real-time RT-PCR test kits--the RealArt HPA coronavirus LC kit (Artus, Hamburg, Germany) and the LightCycler SARS-CoV quantification kit (Roche, Penzberg, Germany)--and a real-time RT-PCR assay for the nucleocapsid (N) gene. Detecting the N-gene RNA might be advantageous due to its high abundance in cells. The kits achieved sensitivities of 70.8% (Artus) and 67.1% (Roche) in 66 specimens from patients with confirmed SARS (samples primarily from the upper and lower respiratory tract and stool). The sensitivity of the N-gene assay was 74.2%. The differences in all of the sensitivities were not statistically significant (P = 0.680 [analysis of variance]). Culture cells initially contained five times more N- than R-gene RNA, but the respective levels converged during 4 days of virus replication. In clinical samples the median concentrations of R- and N-gene RNA, respectively, were 1.2 x 10(6) and 2.8 x 10(6) copies/ml (sputum and endotracheal aspirates), 4.3 x 10(4) and 5.5 x 10(4) copies/ml (stool), and 5.5 x 10(2) and 5.2 x 10(2) copies/sample (throat swabs and saliva). Differences between the samples types were significant but not between the types of target RNA. All (n = 12) samples from the lower respiratory tract tested positive in all tests. In conclusion, the novel assays are more sensitive than the first-generation tests, but they still do not allow a comprehensive ruling out of SARS. Methods for the routine sampling of sputum without infection risk are needed to improve SARS RT-PCR.
Figures
References
-
- Donnelly, C. A., A. C. Ghani, G. M. Leung, A. J. Hedley, C. Fraser, S. Riley, L. J. Abu-Raddad, L. M. Ho, T. Q. Thach, P. Chau, K. P. Chan, T. H. Lam, L. Y. Tse, T. Tsang, S. H. Liu, J. H. B. Kong, E. M. C. Lau, N. M. Ferguson, and R. M. Anderson. 2003. Epidemiological determinants of spread of causal agent of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. Lancet 361:1761-1766. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drosten, C., S. Göttig, S. Schilling, M. Asper, M. Panning, H. Schmitz, and S. Günther. 2002. Rapid detection and quantification of RNA of Ebola and Marburg viruses, Lassa virus, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, Rift Valley fever virus, dengue virus, and yellow fever virus by real-time reverse transcription-PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40:2323-2330. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drosten, C., S. Günther, W. Preiser, S. van der Werf, H. R. Brodt, S. Becker, H. Rabenau, M. Panning, L. Kolesnikova, R. A. Fouchier, A. Berger, A. M. Burguiere, J. Cinatl, M. Eickmann, N. Escriou, K. Grywna, S. Kramme, J. C. Manuguerra, S. Müller, V. Rickerts, M. Stürmer, S. Vieth, H. D. Klenk, A. D. M. E. Osterhaus, H. Schmitz, and H. W. Doerr. 2003. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 348:1967-1976. - PubMed
-
- Ksiazek, T. G., D. Erdman, C. S. Goldsmith, S. R. Zaki, T. Peret, S. Emery, S. Tong, C. Urbani, J. A. Comer, W. Lim, P. E. Rollin, S. F. Dowell, A. E. Ling, C. D. Humphrey, W. J. Shieh, J. Guarner, C. D. Paddock, P. Rota, B. Fields, J. DeRisi, J. Y. Yang, N. Cox, J. M. Hughes, J. W. LeDuc, W. J. Bellini, and L. J. Anderson. 2003. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 348:1953-1966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

