Widespread skin and soft-tissue infections due to two methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains harboring the genes for Panton-Valentine leucocidin
- PMID: 15131173
- PMCID: PMC404676
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.5.2080-2084.2004
Widespread skin and soft-tissue infections due to two methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains harboring the genes for Panton-Valentine leucocidin
Erratum in
- J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Sep;48(9):3461. Somboona, Naraporn S [corrected to Somboonna, Naraporn]
Abstract
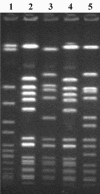
Infections caused by community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) are emerging as a major public health problem. CA-MRSA has been associated previously with skin and soft-tissue infection (SSTI) and with carriage of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) type IV and the Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL) virulence factor. To assess the clonal distribution of PVL-carrying strains and the association with SSTI in the San Francisco Bay area, we surveyed six collections of S. aureus isolates-671 isolates in all-collected between 1997 and 2002 originating from inpatient and outpatient clinical specimens and from a community-based sampling. Isolates were genotyped by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, multilocus restriction fragment typing, and multilocus sequence typing and assayed for the PVL virulence factor. The S. aureus populations showed a high proportion of PVL-carrying strains, with frequencies ranging up to 70% in MRSA isolated from jail inmate patients and 69% in MRSA from patients receiving surgical treatment at an outpatient clinic specializing in treating SSTIs. PVL-carrying isolates were identified in nine clonal groups, but 88.5% of the PVL-carrying MRSA isolates belonged to only two clonal groups. These two clonal groups carried the SCCmec type IV resistance determinant and were more likely than other clonal groups to be recovered from SSTI sites than from other sites (P < 0.0001). There is evidence of clonal replacement over the period from 1999 to 2002, with one of these two clonal groups being supplanted by the other.
Figures
References
-
- Adcock, P. M., P. Pastor, F. Medley, J. E. Patterson, and T. V. Murphy. 1998. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in two child care centers. J. Infect. Dis. 178:577-580. - PubMed
-
- Agresti, A. 2001. Exact inference for categorical data: recent advances and continuing controversies. Stat. Med. 20:2709-2722. - PubMed
-
- Baba, T., F. Takeuchi, M. Kuroda, H. Yuzawa, K. Aoki, A. Oguchi, Y. Nagai, N. Iwama, K. Asano, T. Naimi, H. Kuroda, L. Cui, K. Yamamoto, and K. Hiramatsu. 2002. Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet 359:1819-1827. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2003. Public health dispatch: outbreaks of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin infections—Los Angeles County, California, 2002-2003. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 52:88. - PubMed
-
- Charlebois, E. D., D. R. Bangsberg, N. J. Moss, M. R. Moore, A. R. Moss, H. F. Chambers, and F. Perdreau-Remington. 2002. Population-based community prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the urban poor of San Francisco. Clin. Infect. Dis. 34:425-433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical