Incidence of group C human rotavirus in central Australia and sequence variation of the VP7 and VP4 genes
- PMID: 15131180
- PMCID: PMC404610
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.5.2127-2133.2004
Incidence of group C human rotavirus in central Australia and sequence variation of the VP7 and VP4 genes
Abstract
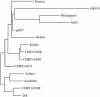
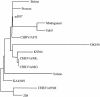
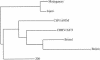
Human group C rotavirus was identified in central Australia in each of eight years over a 16-year period between 1982 and 1997. Cases occurred either sporadically but over a relatively short period of time or as clustered outbreaks. These are the only reports of human group C rotavirus in Australia other than that of a single case reported approximately 1,800 km away in 1982. The electrophoretic genome profiles of isolates were identical for all those identified within the same year but different between those identified in different years. The VP7 genes of four isolates identified in four different years over a 7-year period between 1987 and 1993, and the VP4 genes of two of these isolates showed relatively little variation in genome and deduced amino acid sequence upon comparison of the equivalent genes between isolates. The sequences were also very similar to those from the corresponding genes from most of the human group C rotavirus isolates from other countries. This continues the observation of a high degree of gene sequence conservation among human group C rotaviruses worldwide.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phylogenetic analysis of human group C rotavirus circulating in Brazil reveals a potential unique NSP4 genetic variant and high similarity with Asian strains.Mol Genet Genomics. 2015 Jun;290(3):969-86. doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0971-9. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25501310
-
Genetic variability of VP7, VP4, VP6 and NSP4 genes of common human G1P[8] rotavirus strains circulating in Italy between 2010 and 2014.Virus Res. 2016 Jul 15;220:117-28. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.04.018. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27130628
-
Genetic analysis of G12P[8] rotaviruses detected in the largest U.S. G12 genotype outbreak on record.Infect Genet Evol. 2014 Jan;21:214-9. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Infect Genet Evol. 2014. PMID: 24270016 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected spreading of G12P[8] rotavirus strains among young children in a small area of central Italy.J Med Virol. 2015 Aug;87(8):1292-302. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24180. Epub 2015 Mar 10. J Med Virol. 2015. PMID: 25758365
-
Genetic diversity of G1P[8] rotavirus VP7 and VP8* antigens in Finland over a 20-year period: No evidence for selection pressure by universal mass vaccination with RotaTeq® vaccine.Infect Genet Evol. 2013 Oct;19:51-8. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.06.026. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Infect Genet Evol. 2013. PMID: 23831933 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of Rotaviruses Groups A and C in Egyptian Children and Aquatic Environment.Food Environ Virol. 2015 Feb 11. doi: 10.1007/s12560-015-9184-6. Online ahead of print. Food Environ Virol. 2015. PMID: 25665825
-
Multiple reassortment and interspecies transmission events contribute to the diversity of porcine-like human rotavirus C strains detected in South Korea.Arch Virol. 2022 Nov;167(11):2163-2171. doi: 10.1007/s00705-022-05528-1. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Arch Virol. 2022. PMID: 35840863
-
Detection and characterization of group C rotaviruses in asymptomatic piglets in Ireland.J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Sep;46(9):2973-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00809-08. Epub 2008 Jul 16. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18632912 Free PMC article.
-
First study conducted in Northern India that identifies group C rotavirus as the etiological agent of severe diarrhea in children in Delhi.Virol J. 2017 May 30;14(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0767-8. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28558823 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic analysis of human group C rotavirus circulating in Brazil reveals a potential unique NSP4 genetic variant and high similarity with Asian strains.Mol Genet Genomics. 2015 Jun;290(3):969-86. doi: 10.1007/s00438-014-0971-9. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Mol Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25501310
References
-
- Adah, M. I., A. Wade, M. Oseto, M. Kuzuya, and K. Taniguchi. 2002. Detection of human group C rotaviruses in Nigeria and sequence analysis of their genes encoding VP4, VP6, and VP7 proteins. J. Med. Virol. 66:269-275. - PubMed
-
- Castello, A. A., M. H. Argüelles, G. A. Villegas, A. Olthoff, and G. Glikmann. 2002. Incidence and prevalence of human group C rotavirus infections in Argentina. J. Med. Virol. 67:106-112. - PubMed
-
- Castello, A. A., M. H. Argüelles, G. A. Villegas, N. López, D. P. Ghiringhelli, L. Semorile, and G. Glikmann. 2000. Characterization of human group C rotavirus in Argentina. J. Med. Virol. 62:199-207. - PubMed
-
- Fielding, P. A., P. R. Lambden, E. O. Caul, and I. N. Clarke. 1994. Molecular characterization of the outer capsid spike protein (VP4) gene from human group C rotavirus. Virology 204:442-446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

