Asymptomatic and symptomatic excretion of noroviruses during a hospital outbreak of gastroenteritis
- PMID: 15131210
- PMCID: PMC404621
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.5.2271-2274.2004
Asymptomatic and symptomatic excretion of noroviruses during a hospital outbreak of gastroenteritis
Abstract
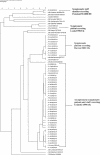
During an investigation of a hospital outbreak of norovirus gastroenteritis identified as being caused by a recombinant genogroup II (rGII-3a) strain, fecal specimens collected from asymptomatic staff and patients were tested by nested PCR. A GII-4 norovirus strain, the predominant strain associated with outbreaks in hospitals over the last few years, was detected in 26 and 33% of asymptomatic staff and patients, respectively. No rGII-3a (Harrow/Mexico) norovirus strains were detected in the samples of asymptomatic staff or patients.
Figures
References
-
- Fankhauser, R. L., S. S. Monroe, J. S. Noel, C. D. Humphrey, J. S. Bresee, U. D. Parashar, T. Ando, and R. I. Glass. 2002. Epidemiologic and molecular trends of “Norwalk-like viruses” associated with outbreaks of gastroenteritis in the United States. J. Infect. Dis. 186:1-7. - PubMed
-
- Fankhauser, R. L., J. S. Noel, S. S. Monroe, T. Ando, and Glass. R. I. 1998. Molecular epidemiology of “Norwalk-like viruses” in outbreaks of gastroenteritis in the United States. J. Infect. Dis. 178:1571-1578. - PubMed
-
- Graham, D. Y., X. Jiang, T. Tanaka, A. R. Opekum, H. P. Madore, and M. K. Estes. 1994. Norwalk virus infection of volunteers: new insights based on improved assays. J. Infect. Dis. 170:34-43. - PubMed
-
- Gray, J. J., C. Cunliff, J. Ball, D. Y. Graham, U. Desselberger, and M. K. Estes. 1994. Detection of immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgA, and IgG Norwalk virus-specific antibodies by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with baculovirus-expressed Norwalk virus capsid antigen in adult volunteers challenged with Norwalk virus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 32:3059-3063. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

