Chronic cholangitis caused by Bordetella hinzii in a liver transplant recipient
- PMID: 15131227
- PMCID: PMC404647
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.5.2335-2337.2004
Chronic cholangitis caused by Bordetella hinzii in a liver transplant recipient
Abstract
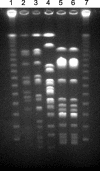
Bordetella hinzii was isolated in four biliary specimens collected over 6 months from a liver transplant recipient with cholangitis. The isolates were resistant to most beta-lactam antibiotics and fluoroquinolones. Molecular typing was performed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. These data add cholangitis to the spectrum of disease manifestations caused by B. hinzii.
Figures
References
-
- Arvand, M., A. J. Klose, D. Schwartz-Porsche, H. Hahn, and C. Wendt. 2001. Genetic variability and prevalence of Bartonella henselae in cats in Berlin, Germany, and analysis of its genetic relatedness to a strain from Berlin that is pathogenic for humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:743-746. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gadea, I., M. Cuenca-Estrella, N. Benito, A. Blanco, M. L. Fernandez-Guerrero, P. L. Valero-Guillen, and F. Soriano. 2000. Bordetella hinzii, a “new” opportunistic pathogen to think about. J. Infect. 40:298-299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

