Parallel synthesis and antimalarial screening of a 4-aminoquinoline library
- PMID: 15132606
- PMCID: PMC1467020
- DOI: 10.1021/cc0340473
Parallel synthesis and antimalarial screening of a 4-aminoquinoline library
Abstract
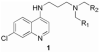
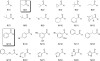
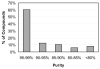
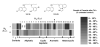
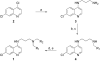
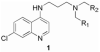
Due to growing problems with drug resistance, there is an outstanding need for new, cost-effective drugs for the treatment of malaria. The 4-aminoquinolines have provided a number of useful antimalarials, and Plasmodium falciparum, the causative organism for the most deadly form of human malaria, is generally slow to develop resistance to these drugs. Therefore, diverse screening libraries of quinolines continue to be useful for antimalarial drug discovery. We report herein the development of an efficient method for producing libraries of 4-aminoquinolines variant in the side chain portion of the molecule. The effects of these substitutions were evaluated by screening this library for activity against P. falciparum, revealing four potent compounds active against drug-resistant strains.
Figures
References
-
- Sachs J, Malaney P. Nature. 2002;415(6872):680–5. - PubMed
-
- Winstanley PA, Breckenridge AM. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1987;81(5):619–27. - PubMed
-
- Diseases, U. W. B. W. S. P. f. R. a. T. i. T . Tropical disease research : progress 1997-98 : fourteenth programme report : malaria / UNDP/WORLD BANK/WHO Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases. World Health Organization; Geneva: 1999. TDR/PR14/MAL/99.1.
-
- O'Neill PM, Bray PG, Hawley SR, Ward SA, Park BK. Pharmacol Ther. 1998;77(1):29–58. - PubMed
-
- Foley M, Tilley L. Pharmacol Ther. 1998;79(1):55–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

