Exposure to cAMP and beta-adrenergic stimulation recruits Ca(V)3 T-type channels in rat chromaffin cells through Epac cAMP-receptor proteins
- PMID: 15133061
- PMCID: PMC1664977
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.061184
Exposure to cAMP and beta-adrenergic stimulation recruits Ca(V)3 T-type channels in rat chromaffin cells through Epac cAMP-receptor proteins
Abstract
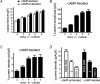
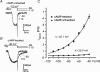
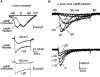
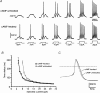
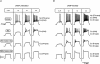
T-type channels are expressed weakly or not at all in adult rat chromaffin cells (RCCs) and there is contrasting evidence as to whether they play a functional role in catecholamine secretion. Here we show that 3-5 days after application of pCPT-cAMP, most RCCs grown in serum-free medium expressed a high density of low-voltage-activated T-type channels without altering the expression and characteristics of high-voltage-activated channels. The density of cAMP-recruited T-type channels increased with time and displayed the typical biophysical and pharmacological properties of low-voltage-activated Ca(2+) channels: (1) steep voltage-dependent activation from -50 mV in 10 mm Ca(2+), (2) slow deactivation but fast and complete inactivation, (3) full inactivation following short conditioning prepulses to -30 mV, (4) effective block of Ca(2+) influx with 50 microM Ni(2+), (5) comparable permeability to Ca(2+) and Ba(2+), and (6) insensitivity to common Ca(2+) channel antagonists. The action of exogenous pCPT-cAMP (200 microM) was prevented by the protein synthesis inhibitor anisomycin and mimicked in most cells by exposure to forskolin and 1-methyl-3-isobutylxanthine (IBMX) or isoprenaline. The protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor H89 (0.3 microM) and the competitive antagonist of cAMP binding to PKA, Rp-cAMPS, had weak or no effect on the action of pCPT-cAMP. In line with this, the selective Epac agonist 8CPT-2Me-cAMP nicely mimicked the action of pCPT-cAMP and isoprenaline, suggesting the existence of a dominant Epac-dependent recruitment of T-type channels in RCCs that may originate from the activation of beta-adrenoceptors. Stimulation of beta-adrenoceptors occurs autocrinally in RCCs and thus, the neosynthesis of low-voltage-activated channels may represent a new form of 'chromaffin cell plasticity', which contributes, by lowering the threshold of action potential firing, to increasing cell excitability and secretory activity during sustained sympathetic stimulation and/or increased catecholamine circulation.
Figures

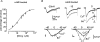
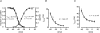


Similar articles
-
An activity-dependent increased role for L-type calcium channels in exocytosis is regulated by adrenergic signaling in chromaffin cells.Neuroscience. 2006 Dec 1;143(2):445-59. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.08.001. Epub 2006 Sep 8. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16962713
-
cAMP increases Ca2+-dependent exocytosis through both PKA and Epac2 in mouse melanotrophs from pituitary tissue slices.J Physiol. 2005 Sep 15;567(Pt 3):799-813. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.090381. Epub 2005 Jun 30. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15994184 Free PMC article.
-
Exchange protein directly activated by cAMP mediates slow delayed-rectifier current remodeling by sustained β-adrenergic activation in guinea pig hearts.Circ Res. 2014 Mar 14;114(6):993-1003. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.302982. Epub 2014 Feb 7. Circ Res. 2014. PMID: 24508724
-
Direct and remote modulation of L-channels in chromaffin cells: distinct actions on alpha1C and alpha1D subunits?Mol Neurobiol. 2004 Feb;29(1):73-96. doi: 10.1385/MN:29:1:73. Mol Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15034224 Review.
-
Cav1.3 and Cav1.2 channels of adrenal chromaffin cells: emerging views on cAMP/cGMP-mediated phosphorylation and role in pacemaking.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jul;1828(7):1608-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.11.013. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23159773 Review.
Cited by
-
ACTH induces Cav3.2 current and mRNA by cAMP-dependent and cAMP-independent mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 25;285(26):20040-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.104190. Epub 2010 Apr 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20424171 Free PMC article.
-
T-type channel-mediated neurotransmitter release.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Apr;466(4):677-87. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1489-z. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24595475 Review.
-
Comparison of Ca2+ currents of chromaffin cells from normotensive Wistar Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rats.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Nov;30(8):1243-50. doi: 10.1007/s10571-010-9566-0. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 21061167 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic hypoxia up-regulates alpha1H T-type channels and low-threshold catecholamine secretion in rat chromaffin cells.J Physiol. 2007 Oct 1;584(Pt 1):149-65. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.132274. Epub 2007 Aug 9. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17690152 Free PMC article.
-
Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP) recruits low voltage-activated T-type calcium influx under acute sympathetic stimulation in mouse adrenal chromaffin cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 9;286(49):42459-42469. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.289389. Epub 2011 Oct 18. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22009744 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

