New technologies for drug delivery across the blood brain barrier
- PMID: 15134486
- PMCID: PMC2711206
- DOI: 10.2174/1381612043384826
New technologies for drug delivery across the blood brain barrier
Abstract
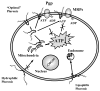
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) efficiently restricts penetration of therapeutic agents to the brain from the periphery. Therefore, discovery of new modalities allowing for effective delivery of drugs and biomacromolecules to the central nervous system (CNS) is of great need and importance for treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. This manuscript focuses on three relatively new strategies. The first strategy involves inhibition of the drug efflux transporters expressed in BBB by Pluronic block copolymers, which allows for the increased transport of the substrates of these transporters to the brain. The second strategy involves the design of nanoparticles conjugated with specific ligands that can target receptors in the brain microvasculature and carry the drugs to the brain through the receptor mediated transcytosis. The third strategy involves artificial hydrophobization of peptides and proteins that facilitates the delivery of these peptides and proteins across BBB. This review discusses the current state, advantages and limitations of each of the three technologies and outlines their future prospects.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CNS disorders--current treatment options and the prospects for advanced therapies.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2008 Nov;34(11):1141-67. doi: 10.1080/03639040802020536. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2008. PMID: 18720140 Review.
-
Drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier.Curr Drug Deliv. 2004 Oct;1(4):361-76. doi: 10.2174/1567201043334542. Curr Drug Deliv. 2004. PMID: 16305398 Review.
-
Concepts, technologies, and practices for drug delivery past the blood-brain barrier to the central nervous system.J Control Release. 2016 Oct 28;240:251-266. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.041. Epub 2015 Dec 24. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26724368 Review.
-
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)-Crossing Strategies for Improved Treatment of CNS Disorders.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024;284:213-230. doi: 10.1007/164_2023_689. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37528323
-
Routes for Drug Translocation Across the Blood-Brain Barrier: Exploiting Peptides as Delivery Vectors.J Pharm Sci. 2017 Sep;106(9):2326-2334. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.04.080. Epub 2017 May 10. J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28501469 Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular delivery of saquinavir in biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles for HIV/AIDS.Pharm Res. 2006 Nov;23(11):2638-45. doi: 10.1007/s11095-006-9101-7. Epub 2006 Sep 13. Pharm Res. 2006. PMID: 16969696
-
Evolution of macromolecular complexity in drug delivery systems.Nat Rev Chem. 2017 Aug;1(8):63. doi: 10.1038/s41570-017-0063. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Nat Rev Chem. 2017. PMID: 31286060 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticulate systems for drug delivery and targeting to the central nervous system.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2011 Dec;17(6):670-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00199.x. Epub 2010 Oct 15. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2011. PMID: 20950327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology prospects in brain therapeutics concerning gene-targeting and nose-to-brain administration.iScience. 2023 Jul 16;26(8):107321. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107321. eCollection 2023 Aug 18. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37554468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Neuroprotective Erythropoietin Modified with a Novel Carrier for the Blood-Brain Barrier.Neurotherapeutics. 2020 Jul;17(3):1184-1196. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00845-2. Neurotherapeutics. 2020. PMID: 32144722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pardridge WM, editor. Methodology, biology and pathology. Cambridge: University Press; 1998. Introduction to the blood-brain barrier.
-
- Mayhan WG. Regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability. Microcirculation. 2001;8(2):89–104. - PubMed
-
- Begley D. The blood-brain barrier: principles for targeting peptides and drugs to the central nervous system. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1996;48(2):136–146. - PubMed
-
- Tamai I, Tsuji A. Transporter-mediated permeation of drugs across the blood-brain barrier. J Pharm Sci. 2000;89(11):1371–1388. - PubMed
-
- Fromm MF. P-glycoprotein: a defense mechanism limiting oral bioavailability and CNS accumulation of drugs. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2000;38(2):69–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

