Bias associated with delayed verification in test accuracy studies: accuracy of tests for endometrial hyperplasia may be much higher than we think!
- PMID: 15137911
- PMCID: PMC419332
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7015-2-18
Bias associated with delayed verification in test accuracy studies: accuracy of tests for endometrial hyperplasia may be much higher than we think!
Abstract
Background: To empirically evaluate bias in estimation of accuracy associated with delay in verification of diagnosis among studies evaluating tests for predicting endometrial hyperplasia.
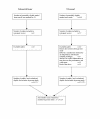
Methods: Systematic reviews of all published research on accuracy of miniature endometrial biopsy and endometrial ultrasonography for diagnosing endometrial hyperplasia identified 27 test accuracy studies (2,982 subjects). Of these, 16 had immediate histological verification of diagnosis while 11 had verification delayed > 24 hrs after testing. The effect of delay in verification of diagnosis on estimates of accuracy was evaluated using meta-regression with diagnostic odds ratio (dOR) as the accuracy measure. This analysis was adjusted for study quality and type of test (miniature endometrial biopsy or endometrial ultrasound).
Results: Compared to studies with immediate verification of diagnosis (dOR 67.2, 95% CI 21.7-208.8), those with delayed verification (dOR 16.2, 95% CI 8.6-30.5) underestimated the diagnostic accuracy by 74% (95% CI 7%-99%; P value = 0.048).
Conclusion: Among studies of miniature endometrial biopsy and endometrial ultrasound, diagnostic accuracy is considerably underestimated if there is a delay in histological verification of diagnosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound scan in predicting endometrial hyperplasia and cancer in postmenopausal bleeding.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1999 May;78(5):447-51. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1999. PMID: 10326893
-
The accuracy of endometrial Pipelle sampling with and without sonographic measurement of endometrial thickness.Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Nov;82(5):727-30. Obstet Gynecol. 1993. PMID: 8414316
-
Endometrial thickness predicts endometrial hyperplasia in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome.Fertil Steril. 2011 Jun 30;95(8):2625-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.04.022. Epub 2011 May 7. Fertil Steril. 2011. PMID: 21550041
-
Ultrasound deserves to play a prominent role in the diagnosis and management of endometrial cancer.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014 May;43(5):483-7. doi: 10.1002/uog.13371. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 24789303 Review. No abstract available.
-
Value of sonography in the diagnosis of abnormal vaginal bleeding.J Clin Ultrasound. 2004 Sep;32(7):348-53. doi: 10.1002/jcu.20049. J Clin Ultrasound. 2004. PMID: 15293302 Review.
References
-
- Fox H. Endometrial hyperplasia: a conceptual and practical approach. Gynaecology Forum. 1996;1:7–9.
-
- Kurman RJ, Kaminski PF, Norris HJ. The behaviour of endometrial hyperplasia: a long-term study of "untreated" hyperplasia in 170 patients. Cancer. 1985;56:403–412. - PubMed
-
- Krampl E, Soby B, Istre O. How representative are pipelle endometrial biopsies? A retrospective analysis of 324 biopsies followed by transcervical resection of the endometrium or hysterectomy. Gynaecol Endosc. 1997;6:277–281. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2508.1997.1210540.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

