Use of a synthetic peptide epitope of Asp f 1, a major allergen or antigen of Aspergillus fumigatus, for improved immunodiagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 15138181
- PMCID: PMC404572
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.11.3.552-558.2004
Use of a synthetic peptide epitope of Asp f 1, a major allergen or antigen of Aspergillus fumigatus, for improved immunodiagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
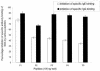
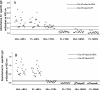
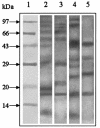
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is an immunologically complex allergic disorder caused by the fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Elevated levels of total immunoglobulin E (IgE), specific IgE, and IgG antibodies in sera are important immunodiagnostic criteria for ABPA. International reference standards or standardized immunodiagnostic assays are not available due to a lack of well-defined diagnostic antigens. The present study was carried out to identify and evaluate the immunodiagnostic relevance of synthetic epitopic peptides of Asp f 1, a major allergen, antigen, or cytotoxin of A. fumigatus. Five overlapping peptides were synthesized from the N terminus of Asp f 1, one of the potential immunodominant regions predicted by algorithmic programs. The 11-amino-acid synthetic peptide (P1) significantly inhibited both IgG binding (89.10% +/- 4.45%) and IgE binding (77.32% +/- 3.38%) of the standardized diagnostic antigen (SDA) (a well-defined pool of diagnostically relevant allergens and antigens of A. fumigatus). With a panel of sera of ABPA patients, allergic patients with skin test negativity to A. fumigatus, and healthy individuals, P1 showed a higher diagnostic efficiency than SDA (specific IgG, 100%; specific IgE, 98.3%). The diagnostic efficiency of P1 could be attributed to the presence of homologous epitopes in various immunodominant allergens or antigens of A. fumigatus. The ability of P1 to induce histamine release from sensitized mast cells and a Th2 type of cytokine profile in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of ABPA patients suggests its potential for use in intradermal testing. P1 could be further explored for development of a standardized, specific, and sensitive immunodiagnostic test for aspergillosis.
Figures
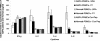
References
-
- Al Moudi, O. S. 2001. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis mimicking pulmonary tuberculosis. Saudi Med. J. 22:708-713. - PubMed
-
- Arruda, L. K., B. J. Mann, and M. D. Chapman. 1992. Selective expression of a major allergen and cytotoxin Asp f 1 in A. fumigatus. J. Immunol. 149:3354-3359. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, B., A. Chetty, A. P. Joshi, and P. U. Sarma. 1990. Identification and characterisation of diagnostically relevant antigens of Aspergillus fumigatus. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 18:13-18. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, B., M. Mukherjee, S. V. Gangal, and P. U. Sarma. 1990. Studies on Aspergillus fumigatus antigens for serodiagnosis. Serodiagn. Immunother. Infect. Dis. 4:183-191.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

