Enhanced surfactant protein and defensin mRNA levels and reduced viral replication during parainfluenza virus type 3 pneumonia in neonatal lambs
- PMID: 15138188
- PMCID: PMC404576
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.11.3.599-607.2004
Enhanced surfactant protein and defensin mRNA levels and reduced viral replication during parainfluenza virus type 3 pneumonia in neonatal lambs
Abstract
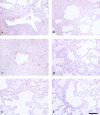
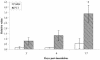
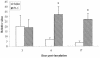
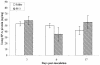
Defensins and surfactant protein A (SP-A) and SP-D are antimicrobial components of the pulmonary innate immune system. The purpose of this study was to determine the extent to which parainfluenza type 3 virus infection in neonatal lambs alters expression of sheep beta-defensin 1 (SBD-1), SP-A, and SP-D, all of which are constitutively transcribed by respiratory epithelia. Parainfluenza type 3 viral antigen was detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in the bronchioles of all infected lambs 3 days postinoculation and at diminished levels 6 days postinoculation, but it was absent 17 days postinoculation. At all times postinoculation, lung homogenates from parainfluenza type 3 virus-inoculated animals had increased SBD-1, SP-A, and SP-D mRNA levels as detected by fluorogenic real-time reverse transcriptase PCR. Protein levels of SP-A in lung homogenates detected by quantitative-competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and protein antigen of SP-A detected by IHC were not altered. These studies demonstrate that parainfluenza type 3 virus infection results in enhanced expression of constitutively transcribed innate immune factors expressed by respiratory epithelia and that this increased expression occurs concurrently with decreased viral replication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surfactant protein D expression in normal and pneumonic ovine lung.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2004 Oct;101(3-4):235-42. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2004.05.004. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2004. PMID: 15350753
-
Human respiratory syncytial virus A2 strain replicates and induces innate immune responses by respiratory epithelia of neonatal lambs.Int J Exp Pathol. 2009 Aug;90(4):431-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2009.00643.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19659901 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of sheep beta-defensin-1 and -2 and interleukin 8 during acute Mannheimia haemolytica pneumonia.Microb Pathog. 2004 Jul;37(1):21-7. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2004.04.003. Microb Pathog. 2004. PMID: 15194156
-
Increased surfactant protein-D and foamy macrophages in smoking-induced mouse emphysema.Respirology. 2007 Mar;12(2):191-201. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2006.01009.x. Respirology. 2007. PMID: 17298450 Review.
-
Surfactant protein A and surfactant protein D variation in pulmonary disease.Immunobiology. 2007;212(4-5):381-416. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Immunobiology. 2007. PMID: 17544823 Review.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and COX-2 cellular expression and distribution after respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza virus infection.Viral Immunol. 2010 Feb;23(1):43-8. doi: 10.1089/vim.2009.0042. Viral Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20121401 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of human beta-defensin-1 (hBD-1) in plasmacytoid dendritic cells (PDC), monocytes, and epithelial cells by influenza virus, Herpes simplex virus, and Sendai virus and its possible role in innate immunity.J Leukoc Biol. 2011 Aug;90(2):343-56. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0209079. Epub 2011 May 6. J Leukoc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21551252 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment with recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor reduces virus replication and inflammation in a perinatal lamb model of respiratory syncytial virus infection.Viral Immunol. 2007 Spring;20(1):188-96. doi: 10.1089/vim.2006.0089. Viral Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17425433 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, expression and activity analyses of five novel duck beta-defensins.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047743. Epub 2012 Oct 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23112840 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological study and detection of Bovine parainfluenza 3 virus in pneumonic sheep lungs using direct immunofluorescence antibody technique.Comp Clin Path. 2021;30(2):301-310. doi: 10.1007/s00580-021-03211-6. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Comp Clin Path. 2021. PMID: 33551715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Darraji, A. M., R. C. Cutlip, and H. D. Lehmkuhl. 1982. Experimental infection of lambs with bovine respiratory syncytial virus and Pasteurella haemolytica: immunofluorescent and electron microscopic studies. Am. J. Vet. Res. 43:230-235. - PubMed
-
- Alkan, F., A. Ozkul, S. Bilge-Dagalp, K. Yesilbag, T. C. Oguzoglu, Y. Akca, and I. Burgu. 2000. Virological and serological studies on the role of PI-3 virus, BRSV, BVDV and BHV-1 on respiratory infections of cattle. I. The detection of etiological agents by direct immunofluorescence technique. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 107:193-195. - PubMed
-
- Awasthi, S., J. J. Coalson, B. A. Yoder, E. Crouch, and R. J. King. 2001. Deficiencies in lung surfactant proteins A and D are associated with lung infection in premature neonatal baboons. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 163:389-397. - PubMed
-
- Belknap, E. B., D. K. Ciszewski, and J. C. Baker. 1995. Experimental respiratory syncytial virus infection in calves and lambs. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 7:285-298. - PubMed
-
- Biragyn, A., P. A. Ruffini, C. A. Leifer, E. Klyushnenkova, A. Shakhov, O. Chertov, A. K. Shirakawa, J. M. Farber, D. M. Segal, J. J. Oppenheim, and L. W. Kwak. 2002. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of dendritic cells by β-defensin 2. Science 298:1025-1029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

