KCNQ/M channels control spike afterdepolarization and burst generation in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 15140933
- PMCID: PMC6729392
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0765-04.2004
KCNQ/M channels control spike afterdepolarization and burst generation in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
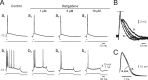
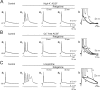
KCNQ channel subunits are widely expressed in peripheral and central neurons, where they give rise to a muscarinic-sensitive, subthreshold, and noninactivating K+ current (M-current). It is generally agreed that activation of KCNQ/M channels contributes to spike frequency adaptation during sustained depolarizations but is too slow to influence the repolarization of solitary spikes. This concept, however, is based mainly on experiments with muscarinic agonists, the multiple effects on membrane conductances of which may overshadow the distinctive effects of KCNQ/M channel block. Here, we have used selective modulators of KCNQ/M channels to investigate their role in spike electrogenesis in CA1 pyramidal cells. Solitary spikes were evoked by brief depolarizing current pulses injected into the neurons. The KCNQ/M channel blockers linopirdine and XE991 markedly enhanced the spike afterdepolarization (ADP) and, in most neurons, converted solitary ("simple") spikes to high-frequency bursts of three to seven spikes ("complex" spikes). Conversely, the KCNQ/M channel opener retigabine reduced the spike ADP and induced regular firing in bursting neurons. Selective block of BK or SK channels had no effect on the spike ADP or firing mode in these neurons. We conclude that KCNQ/M channels activate during the spike ADP and limit its duration, thereby precluding its escalation to a burst. Consequently, down-modulation of KCNQ/M channels converts the neuronal firing pattern from simple to complex spiking, whereas up-modulation of these channels exerts the opposite effect.
Figures






Similar articles
-
M-channels (Kv7/KCNQ channels) that regulate synaptic integration, excitability, and spike pattern of CA1 pyramidal cells are located in the perisomatic region.J Neurosci. 2007 Feb 21;27(8):1853-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4463-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17314282 Free PMC article.
-
KCNQ/Kv7 channel regulation of hippocampal gamma-frequency firing in the absence of synaptic transmission.J Neurophysiol. 2006 May;95(5):3105-12. doi: 10.1152/jn.01083.2005. Epub 2006 Feb 8. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16467425
-
Kv7/KCNQ/M-channels in rat glutamatergic hippocampal axons and their role in regulation of excitability and transmitter release.J Physiol. 2006 Oct 1;576(Pt 1):235-56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.111336. Epub 2006 Jul 13. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16840518 Free PMC article.
-
Neural KCNQ (Kv7) channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;156(8):1185-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00111.x. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19298256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of KCNQ channel activators in management of major depressive disorder.J Affect Disord. 2024 Aug 15;359:364-372. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.05.067. Epub 2024 May 19. J Affect Disord. 2024. PMID: 38772507 Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of near-threshold currents to intrinsic oscillatory activity in rat medial entorhinal cortex layer II stellate cells.J Neurophysiol. 2013 Jan;109(2):445-63. doi: 10.1152/jn.00743.2011. Epub 2012 Oct 17. J Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23076110 Free PMC article.
-
Gq Protein-Coupled Membrane-Initiated Estrogen Signaling Rapidly Excites Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Neurons in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus in Female Mice.Endocrinology. 2016 Sep;157(9):3604-20. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1191. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 27387482 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and functional assessment of two novel KCNQ2 gain-of-function variants Y141N and G239S and effects of amitriptyline treatment.Neurotherapeutics. 2024 Jan;21(1):e00296. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2023.10.006. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Neurotherapeutics. 2024. PMID: 38241158 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic plasticity of Kv7.2/3 channel activity is essential for the induction of tinnitus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jun 11;110(24):9980-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1302770110. Epub 2013 May 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23716673 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Neuroanatomy of the Rat Nucleus Incertus-Medial Septum Tract: Implications for the Cell-Specific Control of the Septohippocampal Pathway.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Feb 25;16:836116. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.836116. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35281300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azouz R, Jensen AM, Yaari Y (1994) Muscarinic modulation of intrinsic burst firing in rat hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 6: 961-966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
