Targeted deletion of the kynurenine aminotransferase ii gene reveals a critical role of endogenous kynurenic acid in the regulation of synaptic transmission via alpha7 nicotinic receptors in the hippocampus
- PMID: 15140935
- PMCID: PMC6729395
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5631-03.2004
Targeted deletion of the kynurenine aminotransferase ii gene reveals a critical role of endogenous kynurenic acid in the regulation of synaptic transmission via alpha7 nicotinic receptors in the hippocampus
Abstract
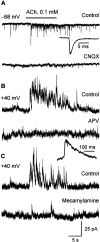
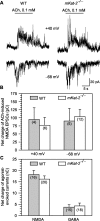
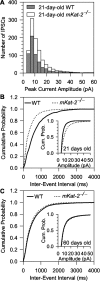
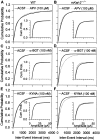
It has been postulated that endogenous kynurenic acid (KYNA) modulates alpha7* nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) and NMDA receptor activities in the brain.a To test this hypothesis, alpha7* nAChR and NMDA receptor functions were studied in mice with a targeted null mutation in the gene encoding kynurenine aminotransferase II (mKat-2-/- mice), an enzyme responsible for brain KYNA synthesis. At 21 postnatal days, mKat-2-/- mice had lower hippocampal KYNA levels and higher spontaneous locomotor activity than wild-type (WT) mice. At this age, alpha7* nAChR activity induced by exogenous application of agonists to CA1 stratum radiatum interneurons was approximately 65% higher in mKat-2-/- than WT mice. Binding studies indicated that the enhanced receptor activity may not have resulted from an increase in alpha7* nAChR number. In 21-d-old mKat-2-/- mice, endogenous alpha7* nAChR activity in the hippocampus was also increased, leading to an enhancement of GABAergic activity impinging onto CA1 pyramidal neurons that could be reduced significantly by acute exposure to KYNA (100 nM). The activities of GABA(A) and NMDA receptors in the interneurons and of alpha3beta4* nAChRs regulating glutamate release onto these neurons were comparable between mKat-2-/- and WT mice. By 60 d of age, KYNA levels and GABAergic transmission in the hippocampus and locomotor activity were similar between mKat-2-/- and WT mice. Our findings that alpha7* nAChRs are major targets for KYNA in the brain may provide insights into the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease, disorders in which brain KYNA levels are increased and alpha7* nAChR functions are impaired.
Figures






References
-
- Adams CE, Broide RS, Chen Y, Winzer-Serhan UH, Henderson TA, Leslie FM, Freedman R (2002) Development of the alpha7 nicotinic cholinergic receptor in rat hippocampal formation. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 139: 175-187. - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque EX, Alkondon M, Pereira EFR, Castro NG, Schrattenholz A, Barbosa CTF, Bonfante-Cabarcas R, Aracava Y, Eisenberg HM, Maelicke A (1997) Properties of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: pharmacological characterization and modulation of synaptic function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280: 1117-1136. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX (2001) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 and alpha4beta2 subtypes differentially control GABAergic input to CA1 neurons in rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 86: 3043-3055. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX (2002) A non-alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulates excitatory input to hippocampal CA1 interneurons. J Neurophysiol 87: 1651-1654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
