The function of neurotrophic factor receptors expressed by the developing adductor motor pool in vivo
- PMID: 15140938
- PMCID: PMC6729401
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0580-04.2004
The function of neurotrophic factor receptors expressed by the developing adductor motor pool in vivo
Abstract
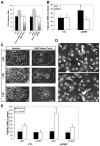
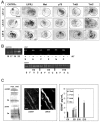
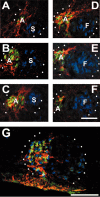
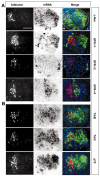
We examined the spatio-temporal relationship between neurotrophic factor receptor (NTF-R) expression and motoneuron (MN) survival in the developing avian spinal cord and observed heterogeneity in the expression of NTF-Rs between, but not within, pools of MNs projecting to individual muscles. We then focused on the role of NTFs in regulating the survival of one motor pool of MNs, all of which innervate a pair of adductor muscles in the thigh and hence compete for survival during the period of programmed cell death (PCD). The complete NTF-R complement of these MNs was analyzed and found to include many, but not all, NTF-Rs. Treatment with exogenous individual NTFs rescued some, but not all, adductor MNs expressing appropriate NTF-Rs. In contrast, administration of multiple NTFs completely rescued adductor MNs from PCD. Additionally, adductor MNs were partially rescued from PCD by NTFs for which they failed to express receptors. NTF-Rs expressed by the nerve but not in the muscle target were capable of mediating survival signals to MNs in trans. Finally, the expression of some NTF-Rs by adductor MNs was not required for MN survival. These studies demonstrate the complexity in NTF regulation of a defined subset of competing MNs and suggest that properties other than NTF-R expression itself can play a role in mediating trophic responses to NTFs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Survival and death of mature avian motoneurons in organotypic slice culture: trophic requirements for survival and different types of degeneration.J Comp Neurol. 2007 Apr 10;501(5):669-90. doi: 10.1002/cne.21157. J Comp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17299760
-
Differential expression of the GDNF family receptors RET and GFRalpha1, 2, and 4 in subsets of motoneurons: a relationship between motoneuron birthdate and receptor expression.J Comp Neurol. 2003 Feb 10;456(3):245-59. doi: 10.1002/cne.10529. J Comp Neurol. 2003. PMID: 12528189
-
Mechanisms of insulin-like growth factor regulation of programmed cell death of developing avian motoneurons.J Neurobiol. 1998 Sep 5;36(3):379-94. J Neurobiol. 1998. PMID: 9733073
-
Neurotrophic modulation of motor neuron development.Neuroscientist. 2009 Feb;15(1):105-16. doi: 10.1177/1073858408324787. Neuroscientist. 2009. PMID: 19218234 Review.
-
Motor neuron trophic factors: therapeutic use in ALS?Brain Res Rev. 2011 Jun 24;67(1-2):1-39. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.10.003. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Brain Res Rev. 2011. PMID: 20971133 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergic effects of EPI-NCSCs and OECs on the donor cells migration, the expression of neurotrophic factors, and locomotor recovery of contused spinal cord of rats.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Mar;55(3):760-9. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0416-2. Epub 2014 Sep 20. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25239519
-
Pool-specific regulation of motor neuron survival by neurotrophic support.J Neurosci. 2011 Aug 3;31(31):11144-58. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2198-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21813676 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase is dynamically expressed on subsets of motor neurons and in the peripheral nervous system.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Mar 10;495(2):202-12. doi: 10.1002/cne.20887. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16435287 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of leukemia inhibitory factor receptor beta or cardiotrophin-1 causes similar deficits in preganglionic sympathetic neurons and adrenal medulla.J Neurosci. 2006 Feb 8;26(6):1823-32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4127-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16467531 Free PMC article.
-
α2-chimaerin is required for Eph receptor-class-specific spinal motor axon guidance and coordinate activation of antagonistic muscles.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 11;35(6):2344-57. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4151-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25673830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Airaksinen MS, Saarma M (2002) The GDNF family: signaling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 383-394. - PubMed
-
- Alexander WS, Rakar S, Robb L, Farley A, Willson TA, Zhang JG, Hartley L, Kikuchi Y, Kojima T, Nomura H, Hasegawa M, Maeda M, Fabri L, Jachno K, Nash A, Metcalf D, Nicola NA, Hilton DJ (1999) Suckling defect in mice lacking the soluble haemopoietin receptor NR6. Curr Biol 9: 605-608. - PubMed
-
- Baloh RH, Tansey MG, Golden JP, Creedon DJ, Heuckeroth RO, Keck CL, Zimonjic DB, Popescu NC, Johnson Jr EM, Milbrandt J (1997) TrnR2, a novel receptor that mediates neurturin and GDNF signaling through Ret. Neuron 18: 793-802. - PubMed
-
- Bottaro DP, Rubin JS, Faletto DL, Chan AM, Kmiecik TE, Vande Woude GF, Aaronson SA (1991) Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science 251: 802-804. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
