Ca2+-binding protein-1 facilitates and forms a postsynaptic complex with Cav1.2 (L-type) Ca2+ channels
- PMID: 15140941
- PMCID: PMC6729388
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5523-03.2004
Ca2+-binding protein-1 facilitates and forms a postsynaptic complex with Cav1.2 (L-type) Ca2+ channels
Abstract
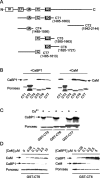
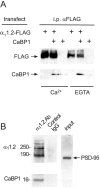
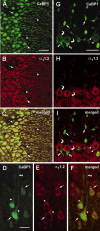
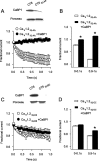
Ca2+-binding protein-1 (CaBP1) is a Ca2+-binding protein that is closely related to calmodulin (CaM) and localized in somatodendritic regions of principal neurons throughout the brain, but how CaBP1 participates in postsynaptic Ca2+ signaling is not known. Here, we describe a novel role for CaBP1 in the regulation of Ca2+ influx through Ca(v)1.2 (L-type) Ca2+ channels. CaBP1 interacts directly with the alpha1 subunit of Ca(v)1.2 at sites that also bind CaM. CaBP1 binding to one of these sites, the IQ domain, is Ca2+ dependent and competitive with CaM binding. The physiological significance of this interaction is supported by the association of Ca(v)1.2 and CaBP1 in postsynaptic density fractions purified from rat brain. Moreover, in double-label immunofluorescence experiments, CaBP1 and Ca(v)1.2 colocalize in numerous cell bodies and dendrites of neurons, particularly in pyramidal cells in the CA3 region of the hippocampus and in the dorsal cortex. In electrophysiological recordings of cells transfected with Ca(v)1.2, CaBP1 greatly prolonged Ca2+ currents, prevented Ca2+-dependent inactivation, and caused Ca2+-dependent facilitation of currents evoked by step depolarizations and repetitive stimuli. These effects contrast with those of CaM, which promoted strong Ca2+-dependent inactivation of Ca(v)1.2 with these same voltage protocols. Our findings reveal how Ca2+-binding proteins, such as CaM and CaBP1, differentially adjust Ca2+ influx through Ca(v)1.2 channels, which may specify diverse modes of Ca2+ signaling in neurons.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Decalmodulation of Cav1 channels by CaBPs.Channels (Austin). 2016;10(1):33-7. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1051273. Epub 2015 Jul 8. Channels (Austin). 2016. PMID: 26155893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential modulation of Ca(v)2.1 channels by calmodulin and Ca2+-binding protein 1.Nat Neurosci. 2002 Mar;5(3):210-7. doi: 10.1038/nn805. Nat Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11865310 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism for divergent regulation of Cav1.2 Ca2+ channels by calmodulin and Ca2+-binding protein-1.J Biol Chem. 2005 Aug 19;280(33):29612-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504167200. Epub 2005 Jun 26. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15980432
-
Competitive and non-competitive regulation of calcium-dependent inactivation in CaV1.2 L-type Ca2+ channels by calmodulin and Ca2+-binding protein 1.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 3;288(18):12680-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.460949. Epub 2013 Mar 25. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23530039 Free PMC article.
-
L-Type Ca2+ Channel Regulation by Calmodulin and CaBP1.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 2;11(12):1811. doi: 10.3390/biom11121811. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944455 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decalmodulation of Cav1 channels by CaBPs.Channels (Austin). 2016;10(1):33-7. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1051273. Epub 2015 Jul 8. Channels (Austin). 2016. PMID: 26155893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex regulation of voltage-dependent activation and inactivation properties of retinal voltage-gated Cav1.4 L-type Ca2+ channels by Ca2+-binding protein 4 (CaBP4).J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 19;287(43):36312-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.392811. Epub 2012 Aug 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22936811 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles of calmodulin and other Ca(2+)-binding proteins in the functional regulation of TRP channels.Pflugers Arch. 2005 Oct;451(1):105-15. doi: 10.1007/s00424-005-1427-1. Epub 2005 May 28. Pflugers Arch. 2005. PMID: 15924238 Review.
-
Calcium Channels in Retinal Function and Disease.Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2022 Sep 15;8:53-77. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-012121-111325. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35650675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CaBP1 regulates Cav1 L-type Ca2+ channels and their coupling to neurite growth and gene transcription in mouse spiral ganglion neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018 Apr;88:342-352. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29548764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bading H, Ginty DD, Greenberg ME (1993) Regulation of gene expression in hippocampal neurons by distinct calcium signaling pathways. Science 260: 181-186. - PubMed
-
- Beck H, Steffens R, Heinemann U, Elger CE (1997) Properties of voltage-activated Ca2+ currents in acutely isolated human hippocampal granule cells. J Neurophysiol 77: 1526-1537. - PubMed
-
- Brown AM, Schwindt PC, Crill WE (1993) Voltage dependence and activation kinetics of pharmacologically defined components of the high-threshold calcium current in rat neocortical neurons. J Neurophysiol 70: 1530-1543. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
