Longitudinal analysis of CD8+ T cells specific for structural and nonstructural hepatitis B virus proteins in patients with chronic hepatitis B: implications for immunotherapy
- PMID: 15140968
- PMCID: PMC415806
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.11.5707-5719.2004
Longitudinal analysis of CD8+ T cells specific for structural and nonstructural hepatitis B virus proteins in patients with chronic hepatitis B: implications for immunotherapy
Abstract
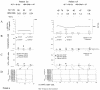
The cytotoxic T-cell response in chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection has been described as weak and mono- or oligospecific in comparison to the more robust virus-specific T-cell response present in resolved infection. However, chronic hepatitis B is a heterogeneous disease with markedly variable levels of virus replication and liver disease activity. Here we analyzed (both directly ex vivo and after in vitro stimulation) the HBV-specific CD8 T-cell responses against structural and nonstructural HBV proteins longitudinally in patients with different patterns of chronic infections. We found that the profiles of virus-specific CD8(+)-T-cell responses during chronic infections are highly heterogeneous and influenced more by the level of HBV replication than by the activity of liver disease. An HBV DNA load of <10(7) copies/ml appears to be the threshold below which circulating multispecific HBV-specific CD8(+) T cells are consistently detected. Furthermore, CD8(+) T cells with different specificities are differentially regulated during chronic infections. HBV core-specific CD8(+) T cells are associated with viral control, while CD8(+) T cells specific for envelope and polymerase epitopes can occasionally be found in the setting of high levels (>10(7) copies) of HBV replication. These findings have implications for the design of immunotherapy for chronic HBV infections.
Figures







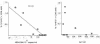

References
-
- Bertoletti, A., A. Costanzo, F. V. Chisari, M. Levrero, M. Artini, A. Sette, A. Penna, T. Giuberti, F. Fiaccadori, and C. Ferrari. 1994. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to a wild-type hepatitis B virus epitope in patients chronically infected by variant viruses carrying substitutions within the epitope. J. Exp. Med. 180:933-943. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertoletti, A., and N. V. Naoumov. 2003. Translation of immunological knowledge into better treatments of chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 39:115-124. - PubMed
-
- Bocher, W., S. Herzog-Hauff, J. Schlaak, K. Meyer zum Buschenfelde, and H. Lohr. 1998. Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen-specific immune responses in acute and chronic hepatitis B or after HBs vaccination: stimulation of the in vitro antibody response by interferon gamma. Hepatology 29:238-244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

