CD40-associated TRAF 6 signaling is required for disease induction in a retrovirus-induced murine immunodeficiency
- PMID: 15141004
- PMCID: PMC415804
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.11.6055-6060.2004
CD40-associated TRAF 6 signaling is required for disease induction in a retrovirus-induced murine immunodeficiency
Abstract
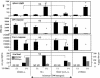
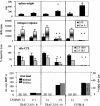
LP-BM5 retrovirus-infected C57BL/6 mice develop splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, hypergammaglobulinemia, and immunodeficiency; thus, this disease has been named mouse AIDS. In this syndrome, CD154/CD40 interactions are required for but do not mediate disease by upregulation of CD80 or CD86. We report here that there is nonetheless a necessity for CD40 signaling competence, specifically an intact tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF 6) binding site.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the CD154-positive and CD40-positive cellular subsets required for pathogenesis in retrovirus-induced murine immunodeficiency.J Virol. 2001 Apr;75(8):3581-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3581-3589.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11264347 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for a continued requirement for CD40/CD40 ligand (CD154) interactions in the progression of LP-BM5 retrovirus-induced murine AIDS.Virology. 1998 Feb 15;241(2):260-8. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8970. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9499800
-
The CD154/CD40 interaction required for retrovirus-induced murine immunodeficiency syndrome is not mediated by upregulation of the CD80/CD86 costimulatory molecules.J Virol. 2002 Dec;76(24):13106-10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.24.13106-13110.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12438641 Free PMC article.
-
Murine AIDS, a key to understanding retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency.Viral Immunol. 1996;9(4):225-39. doi: 10.1089/vim.1996.9.225. Viral Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8978019 Review.
-
Tsl and LP-BM5: a comparison of two murine retrovirus models for HIV.Viral Immunol. 2001;14(2):95-109. doi: 10.1089/088282401750234475. Viral Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11398815 Review.
Cited by
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in murine retrovirus-induced AIDS inhibit T- and B-cell responses in vitro that are used to define the immunodeficiency.J Virol. 2013 Feb;87(4):2058-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01547-12. Epub 2012 Dec 5. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23221564 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CD4 T cells in the pathogenesis of murine AIDS.J Virol. 2006 Jun;80(12):5777-89. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02711-05. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16731917 Free PMC article.
-
Role of a cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte epitope-defined, alternative gag open reading frame in the pathogenesis of a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(7):4308-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4308-4315.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15767431 Free PMC article.
-
Murine AIDS requires CD154/CD40L expression by the CD4 T cells that mediate retrovirus-induced disease: Is CD4 T cell receptor ligation needed?Virology. 2007 Mar 30;360(1):58-71. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.10.002. Epub 2006 Nov 17. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17113120 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy of murine retrovirus-induced acquired immunodeficiency by CD4 T regulatory cell depletion and PD-1 blockade.J Virol. 2011 Dec;85(24):13342-53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00120-11. Epub 2011 Sep 14. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21917983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aziz, D. C., Z. Hanna, and P. Jolicoeur. 1989. Severe immunodeficiency disease induced by a defective murine leukemia virus. Nature (London) 338:505-508. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, G. A., and B. S. Hostager. 2001. Signaling by CD40 and its mimics in B cell activation. Immunol. Res. 24:97-109. - PubMed
-
- Cao, Z., J. Xiong, M. Takeuchi, T. Kurama, and D. V. Goeddel. 1996. TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature 383:443-446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

