Human APOBEC3F is another host factor that blocks human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication
- PMID: 15141007
- PMCID: PMC415831
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.11.6073-6076.2004
Human APOBEC3F is another host factor that blocks human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication
Abstract
Recently, APOBEC3G has been identified as a host factor that blocks retroviral replication. It introduces G to A hypermutations in newly synthesized minus strand viral cDNA at the step of reverse transcription in target cells. Here, we identified the human APOBEC3F protein as another host factor that blocks human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) replication. Similar to APOBEC3G, APOBEC3F also induced G to A hypermutations in HIV genomic DNA, and the viral Vif protein counteracted its activity. Thus, APOBEC family members might have evolved as a general defense mechanism of the body against retroviruses, retrotransposons, and other mobile genetic elements.
Figures
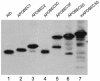




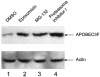
References
-
- Bour, S., and K. Strebel. 2000. HIV accessory proteins: multifunctional components of a complex system. Adv. Pharmacol. 48:75-120. - PubMed
-
- Conticello, S. G., R. S. Harris, and M. S. Neuberger. 2003. The Vif protein of HIV triggers degradation of the human antiretroviral DNA deaminase APOBEC3G. Curr. Biol. 13:2009-2013. - PubMed
-
- Fisher, A. G., B. Ensoli, L. Ivanoff, M. Chamberlain, S. Petteway, L. Ratner, R. C. Gallo, and F. Wong-Staal. 1987. The sor gene of HIV-1 is required for efficient virus transmission in vitro. Science 237:888-893. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

