Glucocorticoids and tumor necrosis factor alpha cooperatively regulate toll-like receptor 2 gene expression
- PMID: 15143169
- PMCID: PMC416411
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.11.4743-4756.2004
Glucocorticoids and tumor necrosis factor alpha cooperatively regulate toll-like receptor 2 gene expression
Abstract
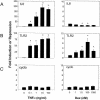
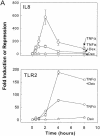
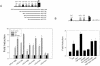
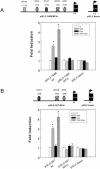
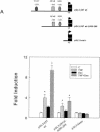
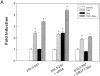
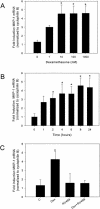
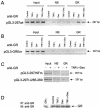
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and glucocorticoids are widely recognized as mutually antagonistic regulators of adaptive immunity and inflammation. Surprisingly, we show here that they cooperatively regulate components of innate immunity. The Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) gene encodes a transmembrane receptor critical for triggering innate immunity. Although TLR2 mRNA and protein are induced by inflammatory molecules such as TNF-alpha, we show that TLR2 is also induced by the anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids in cells where they also regulate MKP-1 mRNA and protein levels. TNF-alpha and glucocorticoids cooperate to regulate the TLR2 promoter, through the involvement of a 3' NF-kappaB site, a STAT-binding element, and a 3' glucocorticoid response element (GRE). Molecular studies show that the IkappaBalpha superrepressor or a STAT dominant negative element prevented TNF-alpha and dexamethasone stimulation of TLR2 promoter. Similarly, an AF-1 deletion mutant of glucocorticoid receptor or ablation of a putative GRE notably reduced the cooperative regulation of TLR2. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, we demonstrate that all three transcription factors interact with both endogenous and transfected TLR2 promoters after stimulation by TNF-alpha and dexamethasone. Together, these studies define novel signaling mechanism for these three transcription factors, with a profound impact on discrimination of innate and adaptive immune responses.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptors 2 and 4, and acute phase cytokine gene expression in dexamethasone and growth hormone treated dairy calves.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2004 Apr;98(3-4):115-25. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2003.10.009. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2004. PMID: 15010221
-
Tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate induces expression of Toll-like receptor 2 in U937 cells: involvement of PKC, ERK, and NF-kappaB.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Mar 4;328(1):70-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.12.144. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 15670752
-
TGF-beta down-regulates IL-1alpha-induced TLR2 expression in murine hepatocytes.J Leukoc Biol. 2004 Jun;75(6):1056-61. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0104108. Epub 2004 Mar 23. J Leukoc Biol. 2004. PMID: 15039464
-
Molecular aspects of glucocorticoid hormone action in rheumatoid arthritis.Cytokines Cell Mol Ther. 2002 Dec;7(2):61-9. doi: 10.1080/13684730412331302081. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12607796 Review.
-
[Mechanism of action of glucocorticoids in asthma].Rev Mal Respir. 1999 Sep;16(4):431-42. Rev Mal Respir. 1999. PMID: 10549054 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Attenuation of cold stress-induced exacerbation of cardiac and adipose tissue pathology and metabolic disorders in a rat model of metabolic syndrome by the glucocorticoid receptor antagonist RU486.Nutr Diabetes. 2016 Apr 25;6(4):e207. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2016.14. Nutr Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 27110688 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-Like Receptor 2 Release by Macrophages: An Anti-inflammatory Program Induced by Glucocorticoids and Lipopolysaccharide.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 23;10:1634. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01634. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31396208 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-Potentiated Spinal Microglia Activation Contributes to Preoperative Anxiety-Induced Postoperative Hyperalgesia.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Aug;54(6):4316-4328. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9976-1. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27339881
-
DAX-1 (dosage-sensitive sex reversal-adrenal hypoplasia congenita critical region on the X-chromosome, gene 1) selectively inhibits transactivation but not transrepression mediated by the glucocorticoid receptor in a LXXLL-dependent manner.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Jul;22(7):1521-34. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0273. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18417736 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroactive Steroids, Toll-like Receptors, and Neuroimmune Regulation: Insights into Their Impact on Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;14(5):582. doi: 10.3390/life14050582. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38792602 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aliprantis, A. O., R. B. Yang, M. R. Mark, S. Suggett, B. Devaux, J. D. Radolf, G. R. Klimpel, P. Godowski, and A. Zychlinsky. 1999. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through toll-like receptor-2. Science 285:736-739. - PubMed
-
- An, H., Y. Yu, M. Zhang, H. Xu, R. Qi, X. Yan, S. Liu, W. Wang, Z. Guo, J. Guo, Z. Qin, and X. Cao. 2002. Involvement of ERK, p38 and NF-kappaB signal transduction in regulation of TLR2, TLR4 and TLR9 gene expression induced by lipopolysaccharide in mouse dendritic cells. Immunology 106:38-45. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang, L., and M. Karin. 2001. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410:37-40. - PubMed
-
- Chrousos, G. P. 1995. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and immune-mediated inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 332:1351-1362. - PubMed
-
- Chuang, T., and R. J. Ulevitch. 2001. Identification of hTLR10: a novel human Toll-like receptor preferentially expressed in immune cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1518:157-161. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
