The homeodomain protein CDP regulates mammary-specific gene transcription and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 15143175
- PMCID: PMC416401
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.11.4810-4823.2004
The homeodomain protein CDP regulates mammary-specific gene transcription and tumorigenesis
Abstract
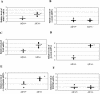
The CCAAT-displacement protein (CDP) has been implicated in developmental and cell-type-specific regulation of many cellular and viral genes. We previously have shown that CDP represses mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) transcription in tissue culture cells. Since CDP-binding activity for the MMTV long terminal repeat declines during mammary development, we tested whether binding mutations could alter viral expression. Infection of mice with MMTV proviruses containing CDP binding site mutations elevated viral RNA levels in virgin mammary glands and shortened mammary tumor latency. To determine if CDP has direct effects on MMTV transcription rather than viral spread, virgin mammary glands of homozygous CDP-mutant mice lacking one of three Cut repeat DNA-binding domains (DeltaCR1) were examined by reverse transcription-PCR. RNA levels of endogenous MMTV as well as alpha-lactalbumin and whey acidic protein (WAP) were elevated. Heterozygous mice with a different CDP mutation that eliminated the entire C terminus and the homeodomain (DeltaC mice) showed increased levels of MMTV, beta-casein, WAP, and alpha-lactalbumin RNA in virgin mammary glands compared to those from wild-type animals. No differences in amounts of WDNM1, epsilon-casein, or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase RNA were observed between the undifferentiated mammary tissues from wild-type and mutant mice, indicating the specificity of this effect. These data show independent contributions of different CDP domains to negative regulation of differentiation-specific genes in the mammary gland.
Figures



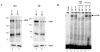

Similar articles
-
Differentiation-induced cleavage of Cutl1/CDP generates a novel dominant-negative isoform that regulates mammary gene expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Oct;26(20):7466-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01083-06. Epub 2006 Aug 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17015474 Free PMC article.
-
CDP is a repressor of mouse mammary tumor virus expression in the mammary gland.J Virol. 2000 Jul;74(14):6348-57. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.14.6348-6357.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10864645 Free PMC article.
-
CDP binding to multiple sites in the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat suppresses basal and glucocorticoid-induced transcription.J Virol. 2002 Mar;76(5):2168-79. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.5.2168-2179.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11836394 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the multifunctional CDP/Cut/Cux homeodomain transcription factor in regulating differentiation, cell growth and development.Gene. 2001 May 30;270(1-2):1-15. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00485-1. Gene. 2001. PMID: 11403998 Review.
-
Stem cells and mammary cancer in mice.Stem Cell Rev. 2005;1(3):215-23. doi: 10.1385/SCR:1:3:215. Stem Cell Rev. 2005. PMID: 17142858 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Ratios of Omega Fatty Acids (AA/EPA+DHA) Modulate Growth, Lipid Peroxidation and Expression of Tumor Regulatory MARBPs in Breast Cancer Cell Lines MCF7 and MDA-MB-231.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 1;10(9):e0136542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136542. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26325577 Free PMC article.
-
Conversion of mouse mammary tumor virus to a lymphomagenic virus.J Virol. 2005 Oct;79(19):12592-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.19.12592-12596.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16160187 Free PMC article.
-
The L2a element is a mouse CD8 silencer that interacts with MAR-binding proteins SATB1 and CDP.Mol Immunol. 2010 Nov-Dec;48(1-3):153-63. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.08.014. Epub 2010 Sep 29. Mol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20884053 Free PMC article.
-
The homeodomain protein Cux1 interacts with Grg4 to repress p27 kip1 expression during kidney development.Gene. 2009 Jun 15;439(1-2):87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.03.014. Epub 2009 Mar 28. Gene. 2009. PMID: 19332113 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation-induced cleavage of Cutl1/CDP generates a novel dominant-negative isoform that regulates mammary gene expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Oct;26(20):7466-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01083-06. Epub 2006 Aug 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17015474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banan, M., I. C. Rojas, W. H. Lee, H. L. King, J. V. Harriss, R. Kobayashi, C. F. Webb, and P. D. Gottlieb. 1997. Interaction of the nuclear matrix-associated region (MAR)-binding proteins, SATB1 and CDP/Cux, with a MAR element (L2a) in an upstream regulatory region of the mouse CD8α gene. J. Biol. Chem. 272:18440-18452. - PubMed
-
- Barberis, A., G. Superti-Furga, and M. Busslinger. 1987. Mutually exclusive interaction of the CCAAT-binding factor and of a displacement protein with overlapping sequences of a histone gene promoter. Cell 50:347-359. - PubMed
-
- Bodmer, R., S. Barbel, S. Sheperd, J. W. Jack, L. Y. Jan, and Y. N. Jan. 1987. Transformation of sensory organs by mutations of the cut locus of D. melanogaster. Cell 51:293-307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
