Signaling specificity by Ras family GTPases is determined by the full spectrum of effectors they regulate
- PMID: 15143186
- PMCID: PMC416418
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.11.4943-4954.2004
Signaling specificity by Ras family GTPases is determined by the full spectrum of effectors they regulate
Abstract
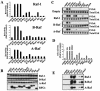
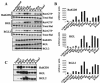
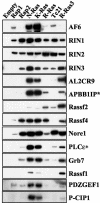
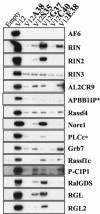
Ras family GTPases (RFGs) regulate signaling pathways that control multiple biological processes. How signaling specificity among the closely related family members is achieved is poorly understood. We have taken a proteomics approach to signaling by RFGs, and we have analyzed interactions of a panel of RFGs with a comprehensive group of known and potential effectors. We have found remarkable differences in the ability of RFGs to regulate the various isoforms of known effector families. We have also identified several proteins as novel effectors of RFGs with differential binding specificities to the various RFGs. We propose that specificity among RFGs is achieved by the differential regulation of combinations of effector families as well as by the selective regulation of different isoforms within an effector family. An understanding of this new level of complexity in the signaling pathways regulated by RFGs is necessary to understand how they carry out their many cellular functions. It will also likely have critical implications in the treatment of human diseases such as cancer.
Figures
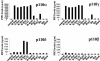

References
-
- Alessi, D. R., P. Cohen, A. Ashworth, S. Cowley, S. J. Leevers, and C. J. Marshall. 1995. Assay and expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAP kinase kinase, and Raf. Methods Enzymol. 255:279-290. - PubMed
-
- Boettner, B., C. Herrmann, and L. Van Aelst. 2001. Ras and Rap1 interaction with AF-6 effector target. Methods Enzymol. 332:151-168. - PubMed
-
- Bos, J. L. 1989. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 49:4682-4689. - PubMed
-
- Bos, J. L., K. De Bruyn, J. Enserink, B. Kuiperij, S. Rangarajan, H. Rehmann, J. Riedl, J. De Rooij, F. Van Mansfeld, and F. Zwartkruis. 2003. The role of Rap1 in integrin-mediated cell adhesion. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31:83-86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
