NHERF2 specifically interacts with LPA2 receptor and defines the specificity and efficiency of receptor-mediated phospholipase C-beta3 activation
- PMID: 15143197
- PMCID: PMC416407
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.11.5069-5079.2004
NHERF2 specifically interacts with LPA2 receptor and defines the specificity and efficiency of receptor-mediated phospholipase C-beta3 activation
Abstract
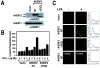
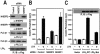
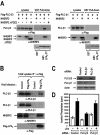
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) activates a family of cognate G protein-coupled receptors and is involved in various pathophysiological processes. However, it is not clearly understood how these LPA receptors are specifically coupled to their downstream signaling molecules. This study found that LPA(2), but not the other LPA receptor isoforms, specifically interacts with Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor2 (NHERF2). In addition, the interaction between them requires the C-terminal PDZ domain-binding motif of LPA(2) and the second PDZ domain of NHERF2. Moreover, the stable expression of NHERF2 potentiated LPA-induced phospholipase C-beta (PLC-beta) activation, which was markedly attenuated by either a mutation in the PDZ-binding motif of LPA(2) or by the gene silencing of NHERF2. Using its second PDZ domain, NHERF2 was found to indirectly link LPA(2) to PLC-beta3 to form a complex, and the other PLC-beta isozymes were not included in the protein complex. Consistently, LPA(2)-mediated PLC-beta activation was specifically inhibited by the gene silencing of PLC-beta3. In addition, NHERF2 increases LPA-induced ERK activation, which is followed by cyclooxygenase-2 induction via a PLC-dependent pathway. Overall, the results suggest that a ternary complex composed of LPA(2), NHERF2, and PLC-beta3 may play a key role in the LPA(2)-mediated PLC-beta signaling pathway.
Figures





References
-
- An, S., T. Bleu, O. G. Hallmark, and E. J. Goetzl. 1998. Characterization of a novel subtype of human G protein-coupled receptor for lysophosphatidic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 273:7906-7910. - PubMed
-
- Arthur, J. F., S. J. Matkovich, C. J. Mitchell, T. J. Biden, and E. A. Woodcock. 2001. Evidence for selective coupling of α1-adrenergic receptors to phospholipase C-β1 in rat neonatal cardiomyocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 276:37341-37346. - PubMed
-
- Bandoh, K., J. Aoki, A. Taira, M. Tsujimoto, H. Arai, and K. Inoue. 2000. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptors of the EDG family are differentially activated by LPA species: structure-activity relationship of cloned LPA receptors. FEBS Lett. 478:159-165. - PubMed
-
- Bandoh, K., J. Aoki, H. Hosono, S. Kobayashi, T. Kobayashi, K. Murakami-Murofushi, M. Tsujimoto, H. Arai, and K. Inoue. 1999. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel human G-protein-coupled receptor, EDG7, for lysophosphatidic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 274:27776-27785. - PubMed
-
- Beekman, A., B. Helfrich, P. A. Bunn, Jr., and L. E. Heasley. 1998. Expression of catalytically inactive phospholipase C-β disrupts phospholipase C-β and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and inhibits small cell lung cancer growth. Cancer Res. 58:910-913. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
