Cornelia de Lange syndrome is caused by mutations in NIPBL, the human homolog of Drosophila melanogaster Nipped-B
- PMID: 15146186
- PMCID: PMC4902017
- DOI: 10.1038/ng1364
Cornelia de Lange syndrome is caused by mutations in NIPBL, the human homolog of Drosophila melanogaster Nipped-B
Abstract
Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS; OMIM 122470) is a dominantly inherited multisystem developmental disorder characterized by growth and cognitive retardation; abnormalities of the upper limbs; gastroesophageal dysfunction; cardiac, ophthalmologic and genitourinary anomalies; hirsutism; and characteristic facial features. Genital anomalies, pyloric stenosis, congenital diaphragmatic hernias, cardiac septal defects, hearing loss and autistic and self-injurious tendencies also frequently occur. Prevalence is estimated to be as high as 1 in 10,000 (ref. 4). We carried out genome-wide linkage exclusion analysis in 12 families with CdLS and identified four candidate regions, of which chromosome 5p13.1 gave the highest multipoint lod score of 2.7. This information, together with the previous identification of a child with CdLS with a de novo t(5;13)(p13.1;q12.1) translocation, allowed delineation of a 1.1-Mb critical region on chromosome 5 for the gene mutated in CdLS. We identified mutations in one gene in this region, which we named NIPBL, in four sporadic and two familial cases of CdLS. We characterized the genomic structure of NIPBL and found that it is widely expressed in fetal and adult tissues. The fly homolog of NIPBL, Nipped-B, facilitates enhancer-promoter communication and regulates Notch signaling and other developmental pathways in Drosophila melanogaster.
Figures

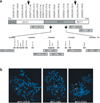
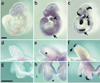
References
-
- de Lange C. Sur un type nouveau de dégénératio (typus Amstelodamensis) Arch. Méd. Enfants. 1933;36:713–719.
-
- Jackson L, Kline AD, Barr MA, Koch S. de Lange syndrome: a clinical review of 310 individuals. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1993;47:940–946. - PubMed
-
- Ireland M, Donnai D, Burn J. Brachmann-de Lange syndrome. Delineation of the clinical phenotype. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1993;47:959–964. - PubMed
-
- Opitz JM. The Brachmann-de Lange syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1985;22:89–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

