Stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma cell model system with multiple metastatic potentials established through consecutive in vivo selection and studies on metastatic characteristics
- PMID: 15146329
- PMCID: PMC12161865
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-004-0564-9
Stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma cell model system with multiple metastatic potentials established through consecutive in vivo selection and studies on metastatic characteristics
Abstract
Purpose: To establish a "stepwise metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell model system" for in-depth study of the underlying mechanisms of HCC metastasis.
Methods: Using MHCC97- a metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line reported in 1999-as the parent cells, we subsequently established three cell lines (MHCC97-L, HMCC97-H, and HCCLM3) with increasing spontaneous metastatic potential. Now, the fourth cell line with unique multiple metastatic characteristics has been established by six rounds of in vivo selection.
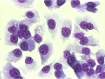
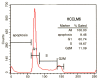
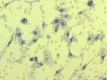
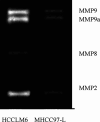
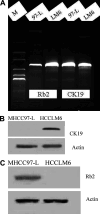
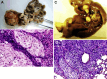
Results: This cell line, designated as HCCLM6, is a polygonal epithelial cell with hypotriploid karyotype, the modal chromosomes are 55-58, and marker chromosomal abnormalities include i(1) (q10), i(8)(q10), der (4) t(4;8)(q31;q22), i(X)(q10). The cell population doubling time was 32 h. Fluorescent PCR showed HBV DNA integration in the cellular genome. Thirty-five days after HCCLM6 was injected subcutaneously into BALB/c nude mice, prominent lung metastases occurred in 100% of the recipient animals. When tumor tissue was orthotopically implanted into the liver of nude mouse, widespread loco-regional and pulmonary metastases occurred. Inoculation of this cell into the footpad of nude mice also produced 75% regional lymph node metastasis. Compared with MHCC97-L which was not metastastatic via subcutaneous or footpad inoculation and 40% metastatic via orthotopic inoculation, HCCLM6 had increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-2 and MMP-9) and cytokeratin 19 (CK19), and decreased expression of Rb2/p130. The establishment of this new cell line has completed our stepwise metastatic HCC cell mode system, which was characterized by a similar genetic background but with significant differences in spontaneous metastasis behavior.
Conclusions: The study supports the theory that cancer metastasis is a highly selective dynamic process and the cell model system could be a useful platform for the study of HCC metastasis.
Figures
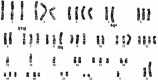
References
-
- Albini A, Iwamoto Y, Kleinman HK, Martin GR, Aaronson SA, Kozlowski JM, McEwan RN (1987) A rapid in vitro assay for quantitating the invasive potential of tumor cells. Cancer Res 47:3239–3245 - PubMed
-
- Baldi A, Esposito V, De Luca A, Fu Y, Meoli I, Giordano GG, Caputi M, Baldi F, Giordano A (1997) Differential expression of Rb2/p130 and p107 in normal human tissue and in primary lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 3:1691–1697 - PubMed
-
- Ding SJ, Li Y, Shao XX, Zhou H, Zeng R, Tang ZY, Xia QC (2004a) Proteome analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell strains, MHCC97-H and MHCC97-L, with different metastasis potentials. Proteomics 4:982–994 - PubMed
-
- Ding SJ, Li Y, Tan YX, Jian MR, Tian B, Liu YK, Shao XX., Ye SL, Wu JR, Zeng R, Wang HY, Tang ZY, Xia QC (2004b) From proteomic analysis to clinical significance: overexpression of cytokeratin 19 correlates with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Mol Cell Proteomics 3:73–81 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

