Fucoidan derived from Cladosiphon okamuranus Tokida ameliorates murine chronic colitis through the down-regulation of interleukin-6 production on colonic epithelial cells
- PMID: 15147344
- PMCID: PMC1809061
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02462.x
Fucoidan derived from Cladosiphon okamuranus Tokida ameliorates murine chronic colitis through the down-regulation of interleukin-6 production on colonic epithelial cells
Abstract
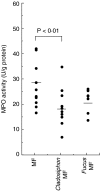
Our previous study indicated that the interleukin (IL)-6/STAT-3 signal was up-regulated in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in both humans and animal models. We also discovered phosphorylated STAT-3 in the nucleus of the colonic epithelial cells in IBD mice. Intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) have been shown to secrete IL-6. Therefore, the secretion of IL-6 from IEC may be one of the mechanisms of STAT-3 phosphorylation in IEC during the pathogenesis of IBD, and inhibition of IL-6 production by IEC may be beneficial in preventing IBD. We examined the preventative effect of various types of fucoidans on IL-6 production in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated murine colonic epithelial cells line, CMT-93, in vitro. We also determined in vivo the effect of fucoidans on murine chronic colitis induced with dextran sodium sulphate. Among fucoidans, those from Cladosiphon okamuranus Tokida and Kjellmaniella crassifolia inhibited IL-6 production in CMT-93 cells with the down-regulation of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation. Analysis of the effect of fucoidan on murine colitis in vivo showed that the disease activity index and myeloperoxidase activity decreased in mice fed Cladosiphon fucoidan, but not Fucus fucoidan. Cytokine profiles in colonic lamina propria indicated that the synthesis of interferon (IFN)-gamma and IL-6 decreased and that of IL-10 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta increased in mice fed Cladosiphon fucoidan, compared with mice fed a standard diet or Fucus fucoidan. The levels of IL-6 mRNA in colonic epithelial cells was lower in colitis-induced Balb/c mice fed Cladosiphon fucoidan than those fed a standard diet. Fucoidan improves murine chronic colitis by down-regulating the synthesis of IL-6 in the colonic epithelial cells. Fucoidan derived from C. o. Tokida may be useful as a dietary substance for the patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Figures






Similar articles
-
IL-15 protects intestinal epithelial cells.Eur J Immunol. 2006 Oct;36(10):2691-9. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535173. Eur J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16981178
-
Essential roles of IL-6 trans-signaling in colonic epithelial cells, induced by the IL-6/soluble-IL-6 receptor derived from lamina propria macrophages, on the development of colitis-associated premalignant cancer in a murine model.J Immunol. 2010 Feb 1;184(3):1543-51. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0801217. Epub 2009 Dec 30. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20042582
-
Dietary rutin, but not its aglycone quercetin, ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in mice: attenuation of pro-inflammatory gene expression.Biochem Pharmacol. 2005 Feb 1;69(3):395-406. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2004.10.015. Epub 2004 Dec 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15652231
-
Biodegradable microspheres targeting mucosal immune-regulating cells: new approach for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.J Gastroenterol. 2003 Mar;38 Suppl 15:59-62. J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12698874 Review.
-
Mucosal T cells as a target for treatment of IBD.J Gastroenterol. 2003 Mar;38 Suppl 15:48-50. J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12698871 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of oral administration of fucoidan extracted from Cladosiphon okamuranus on tumor growth and survival time in a tumor-bearing mouse model.Mar Drugs. 2012 Oct;10(10):2337-2348. doi: 10.3390/md10102337. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Mar Drugs. 2012. PMID: 23170088 Free PMC article.
-
L-fucose reduces gut inflammation due to T-regulatory response in Muc2 null mice.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 30;17(12):e0278714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278714. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36584066 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Fucoidan Pharmaceutical Formulations and Their Potential Application in Oncology-A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jul 29;15(15):3242. doi: 10.3390/polym15153242. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fucoidan as a marine anticancer agent in preclinical development.Mar Drugs. 2014 Jan 28;12(2):851-70. doi: 10.3390/md12020851. Mar Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24477286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brown Seaweed Food Supplementation: Effects on Allergy and Inflammation and Its Consequences.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 29;13(8):2613. doi: 10.3390/nu13082613. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34444774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duchmann R, Schmitt E, Knolle P, et al. Tolerance towards resident intestinal flora in mice is aborogated in experimental colitis and restored by treatment with interleukin-10 or antibodies to interleukin-12. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26:934–8. - PubMed
-
- Sadlack B, Merz H, Schorle H, et al. Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell. 1993;75:253–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

