Characterization of a nudix hydrolase from Deinococcus radiodurans with a marked specificity for (deoxy)ribonucleoside 5'-diphosphates
- PMID: 15147580
- PMCID: PMC428907
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2091-5-7
Characterization of a nudix hydrolase from Deinococcus radiodurans with a marked specificity for (deoxy)ribonucleoside 5'-diphosphates
Abstract
Background: Nudix hydrolases form a protein family whose function is to hydrolyse intracellular nucleotides and so regulate their levels and eliminate potentially toxic derivatives. The genome of the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans encodes 25 nudix hydrolases, an unexpectedly large number. These may contribute to radioresistance by removing mutagenic oxidised and otherwise damaged nucleotides. Characterisation of these hydrolases is necessary to understand the reason for their presence. Here, we report the cloning and characterisation of the DR0975 gene product, a nudix hydrolase that appears to be unique to this organism.
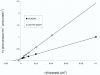
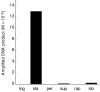
Results: The DR0975 gene was cloned and expressed as a 20 kDa histidine-tagged recombinant product in Escherichia coli. Substrate analysis of the purified enzyme showed it to act primarily as a phosphatase with a marked preference for (deoxy)nucleoside 5'-diphosphates (dGDP > ADP > dADP > GDP > dTDP > UDP > dCDP > CDP). Km for dGDP was 110 microM and kcat was 0.18 s-1 under optimal assay conditions (pH 9.4, 7.5 mM Mg2+). 8-Hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine 5'-diphosphate (8-OH-dGDP) was also a substrate with a Km of 170 microM and kcat of 0.13 s-1. Thus, DR0975 showed no preference for 8-OH-dGDP over dGDP. Limited pyrophosphatase activity was also observed with NADH and some (di)adenosine polyphosphates but no other substrates. Expression of the DR0975 gene was undetectable in logarithmic phase cells but was induced at least 30-fold in stationary phase. Superoxide, but not peroxide, stress and slow, but not rapid, dehydration both caused a slight induction of the DR0975 gene.
Conclusion: Nucleotide substrates for nudix hydrolases conform to the structure NDP-X, where X can be one of several moieties. Thus, a preference for (d)NDPs themselves is most unusual. The lack of preference for 8-OH-dGDP over dGDP as a substrate combined with the induction in stationary phase, but not by peroxide or superoxide, suggests that the function of DR09075 may be to assist in the recycling of nucleotides under the very different metabolic requirements of stationary phase. Thus, if DR0975 does contribute to radiation resistance, this contribution may be indirect.
Figures
References
-
- McLennan AG. The MutT motif family of nucleotide phosphohydrolases in man and human pathogens. Int J Mol Med. 1999;4:79–89. - PubMed
-
- Fisher DI, Safrany ST, Strike P, McLennan AG, Cartwright JL. Nudix hydrolases that degrade dinucleoside and diphosphoinositol polyphosphates also have 5-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) pyrophosphatase activity that generates the glycolytic activator ribose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:47313–47317. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209795200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

