Nitric oxide proxies and ocular perfusion pressure in primary open angle glaucoma
- PMID: 15148207
- PMCID: PMC1772173
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2003.028357
Nitric oxide proxies and ocular perfusion pressure in primary open angle glaucoma
Abstract
Background: To investigate the levels of nitric oxide (NO) markers in plasma and aqueous humour of patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) and their relation to ocular perfusion pressure.
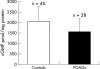
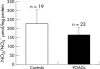
Methods: Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) and nitrite (NO(2)(-)) were determined in plasma and aqueous humour of 38 patients with POAG and 46 controls. Blood pressure and IOP were measured to calculate ocular perfusion pressure (PP).
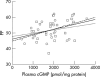
Results: cGMP and NO(2)(-) plasma levels were significantly decreased in glaucoma patients compared with controls (p = 0.001 v p = 0.004). In the aqueous humour of subjects with POAG, cGMP and NO(2)(-) concentrations were also lower than in normal eyes (p = 0.0001 v p = 0.001). There was a linear association between cGMP in plasma and aqueous humour in glaucomas and controls (r = 0.514, p = 0.029 and r = 0.558, p = 0.004) and this relation differed in the two groups (p = 0.003). Considering glaucoma patients with controls, a positive correlation was found between cGMP and PP (r = 0.379, p = 0.01) and between NO(2)(-) and PP (r = 0.339, p = 0.040). The cGMP/PP correlation was of borderline statistical significance in controls (p = 0.050), whereas it did not attain statistical significance in POAG, as well as the association between NO(2)(-) and PP when glaucomas and controls were considered separately.
Conclusions: The authors found alterations of NO markers in the plasma and aqueous humour of glaucoma patients. Primary or secondary impaired NO balance could alter ocular perfusion pressure.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Biochemical markers of the L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway in the aqueous humour in glaucoma patients.Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2002 Apr;80(2):191-5. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0420.2002.800214.x. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2002. PMID: 11952488
-
Ocular haemodynamics and nitric oxide in normal pressure glaucoma.Acta Ophthalmol Scand Suppl. 2000;(232):37-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0420.2000.tb01093.x. Acta Ophthalmol Scand Suppl. 2000. PMID: 11235526
-
Correlation of endothelin-1 concentration in aqueous humor with intraocular pressure in primary open angle and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Oct 23;53(11):7336-42. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10216. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 23036995
-
[Ocular blood flow regulation in glaucoma - examination with the ocular pressure flow analyzer (OPFA)].Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2015 Feb;232(2):152-61. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1396210. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2015. PMID: 25700253 Review. German.
-
Specific Biomarkers in the Aqueous Humour of Glaucoma Patients.Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2022 Feb;239(2):169-176. doi: 10.1055/a-1690-7468. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2022. PMID: 35211939 Review. English, German.
Cited by
-
Association of eNOS and HSP70 gene polymorphisms with glaucoma in Pakistani cohorts.Mol Vis. 2010 Jan 11;16:18-25. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20069064 Free PMC article.
-
A topical nitric oxide-releasing dexamethasone derivative: effects on intraocular pressure and ocular haemodynamics in a rabbit glaucoma model.Br J Ophthalmol. 2006 Nov;90(11):1414-9. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2006.099838. Epub 2006 Aug 16. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006. PMID: 16914472 Free PMC article.
-
PITX2 is involved in stress response in cultured human trabecular meshwork cells through regulation of SLC13A3.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Sep 29;52(10):7625-33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6967. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21873665 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged postocclusive hyperemia response in patients with normal-tension glaucoma.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Dec 11;20:2607-16. doi: 10.12659/MSM.891069. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 25502623 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Function Changes of the Porcine Distal Outflow Tract in Response to Nitric Oxide.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Oct 1;59(12):4886-4895. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-24943. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lincoln J, Hoyle CHV, Burnstock G. Nitric Oxide in health and disease. Cambridge University Press, 1997.
-
- Qi X, Guy J. Localization of NADPH diaphorase/nitric oxide synthase in the optic nerve of the normal guinea pig: a light and electron microscopic study. J Comp Neurol 1996;370:396–404. - PubMed
-
- Neufeld AH, Hernandez MR, Gonzalez M. Nitric oxide synthase in the human glaucomatous optic nerve head. Arch Ophthalmol 1997;115:497–503. - PubMed
-
- Haefliger IO, Flammer J, Lüscher TF. Nitric oxide and endothelin 1 are important regulators of human ophthalmic artery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1992;33:2340–3. - PubMed
-
- Haefliger IO, Flammer J, Lüscher TF. Heterogeneity of endothelium-dependent regulation in ophthalmic and ciliary arteries. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1993;34:1722–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
