Enhanced fidelity for rejoining radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in the G2 phase of Chinese hamster ovary cells
- PMID: 15148355
- PMCID: PMC419594
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh586
Enhanced fidelity for rejoining radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in the G2 phase of Chinese hamster ovary cells
Abstract
The influence of cell cycle phase on the fidelity of DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair is largely unknown. We investigated the rejoining of correct and incorrect DSB ends in synchronized populations of Chinese hamster ovary cells irradiated with 80 Gy X-rays. A specialized pulsed-field gel electrophoresis assay based on quantitative Southern hybridization of individual large restriction fragments was employed to measure correct DSB rejoining by monitoring restriction fragment reconstitution. Total DSB repair, representing both correct and incorrect rejoining, was analyzed using conventional pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. We present evidence that restriction fragment reconstitution is more efficient in G2 than in G1, suggesting that DSB rejoining in G2 proceeds with higher fidelity. DNA-dependent protein kinase-deficient V3 and xrs-6 cells show impaired restriction fragment reconstitution in G1 and G2 compared with wild-type AA8 and K1 cells, demonstrating that the enhanced fidelity of DSB rejoining in G2 occurs by non- homologous end joining. Additionally, homologous recombination-deficient irs1SF and wild-type cells show identical DSB rejoining in G1 and G2. We propose that structural characteristics of G2 phase chromatin, such as the cohesion of sister chromatids in replicated chromatin, limit the mobility of radiation-induced break ends and enhance the fidelity of DSB rejoining.
Figures


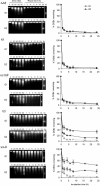
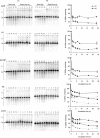
References
-
- Olive P.L. (1998) The role of DNA single- and double-strand breaks in cell killing by ionizing radiation. Radiat. Res., 150, S42–S51. - PubMed
-
- Hoeijmakers J.H. (2001) Genome maintenance mechanisms for preventing cancer. Nature, 411, 366–374. - PubMed
-
- van Gent D.C., Hoeijmakers,J.H. and Kanaar,R. (2001) Chromosomal stability and the DNA double-stranded break connection. Nature Rev. Genet., 2, 196–206. - PubMed
-
- Jeggo P.A. (1998) DNA breakage and repair. In Hall,J.C., Dunlap,J.C., Friedmann,T. and Gianelli,F. (eds), Advances in Genetics. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, Vol. 38, pp. 185–218. - PubMed
-
- Smith G.C. and Jackson,S.P. (1999) The DNA-dependent protein kinase. Genes Dev., 13, 916–934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

