Role of Polo-like kinase in the degradation of early mitotic inhibitor 1, a regulator of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome
- PMID: 15148369
- PMCID: PMC419535
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0402442101
Role of Polo-like kinase in the degradation of early mitotic inhibitor 1, a regulator of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome
Abstract
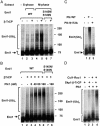
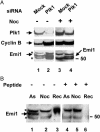
Early mitotic inhibitor 1 (Emi1) inhibits the activity of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), which is a multisubunit ubiquitin ligase that targets mitotic regulators for degradation in exit from mitosis. Levels of Emi1 oscillate in the cell cycle: it accumulates in the S phase and is rapidly degraded in prometaphase. The degradation of Emi1 in early mitosis is necessary for the activation of APC/C in late mitosis. Previous studies have shown that Emi1 is targeted for degradation in mitosis by a Skp1-Cullin1 F-box protein (SCF) ubiquitin ligase complex that contains the F-box protein beta-TrCP. As with other substrates of SCF(beta-TrCP), the phosphorylation of Emi1 on a DSGxxS sequence is required for this process. However, the protein kinase(s) involved has not been identified. We find that Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1), a protein kinase that accumulates in mitosis, markedly stimulates the ligation of Emi1 to ubiquitin by purified SCF(beta-TrCP). Cdk1-cyclin B, another major mitotic protein kinase, has no influence on this process by itself but stimulates the action of Plk1 at low, physiological concentrations. Plk1 phosphorylates serine residues in the DSGxxS sequence of Emi1, as suggested by the reduced phosphorylation of a derivative in which the two serines were mutated to nonphosphorylatable amino acids. Transfection with an small interfering RNA duplex directed against Plk1 caused the accumulation of Emi1 in mitotically arrested HeLa cells. It is suggested that phosphorylation of Emi1 by Plk1 is involved in its degradation in mitosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plk1 regulates activation of the anaphase promoting complex by phosphorylating and triggering SCFbetaTrCP-dependent destruction of the APC Inhibitor Emi1.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Dec;15(12):5623-34. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-07-0598. Epub 2004 Oct 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15469984 Free PMC article.
-
The evi5 oncogene regulates cyclin accumulation by stabilizing the anaphase-promoting complex inhibitor emi1.Cell. 2006 Jan 27;124(2):367-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.038. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16439210
-
Cyclin A2-cyclin-dependent kinase 2 cooperates with the PLK1-SCFbeta-TrCP1-EMI1-anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome axis to promote genome reduplication in the absence of mitosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;29(24):6500-14. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00669-09. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19822658 Free PMC article.
-
Polo-like kinase 1: target and regulator of anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome-dependent proteolysis.Cancer Res. 2006 Jul 15;66(14):6895-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0358. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16849530 Review.
-
Mechanisms and regulation of the degradation of cyclin B.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999 Sep 29;354(1389):1571-5; discussion 1575-6. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1999.0500. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1999. PMID: 10582242 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The phosphorylation-dependent regulation of nuclear SREBP1 during mitosis links lipid metabolism and cell growth.Cell Cycle. 2016 Oct 17;15(20):2753-65. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1220456. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27579997 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Regulatory Mechanisms of N-Myc on Cell Cycle.Molecules. 2023 Jan 23;28(3):1141. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031141. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor inhibition by genomically integrated inducible RNAi-cassettes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(16):4527-36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl628. Epub 2006 Aug 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16945954 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor suppressor CYLD regulates entry into mitosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 May 22;104(21):8869-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703268104. Epub 2007 May 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17495026 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of gene expression-based pharmacodynamic biomarker for a p53 context-specific anti-tumor drug Wee1 inhibitor.Mol Cancer. 2009 Jun 8;8:34. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-8-34. Mol Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19500427 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

