Inhibition of acute graft-versus-host disease with retention of graft-versus-tumor effects by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib
- PMID: 15148407
- PMCID: PMC419567
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0401563101
Inhibition of acute graft-versus-host disease with retention of graft-versus-tumor effects by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Aug 24;101(34):12777
Abstract
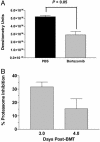
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) represents a major hurdle impeding the efficacy of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation (BMT). Bortezomib is a proteasome inhibitor that was recently approved for treatment of myeloma. We found that bortezomib potently inhibited in vitro mixed lymphocyte responses and promoted the apoptosis of alloreactive T cells. Bortezomib given at the time of allogeneic BMT in mice resulted in significant protection from acute GVHD. Reductions in GVHD-associated parameters and biological evidence of proteasome inhibition were observed with this regimen but with no adverse effects on long-term donor reconstitution. Assessment of graft-versus-tumor responses in advanced leukemia-bearing mice demonstrated that only the combination of allogeneic BMT and T cells with bortezomib promoted significant increases in survival. Increased cytotoxic T cell killing of the tumor was also observed. Thus, the combination of proteasome inhibition with selective immune attack can markedly increase the efficacy of BMT in cancer.
Figures
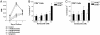
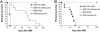
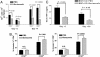
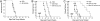

References
-
- Ferrara, J. L., Deeg, H. & Burakoff, S. J. (1997) Graft-versus-Host Disease (Marcel Decker, New York).
-
- Graubert, T. A., Russell, J. H. & Ley, T. J. (1996) Blood 87, 1232–1237. - PubMed
-
- Nestel, F. P., Greene, R. N., Kichian, K., Ponka, P. & Lapp, W. S. (2000) Blood 96, 1836–1843. - PubMed
-
- Welniak, L. A., Blazar, B. R., Wiltrout, R. H., Anver, M. R. & Murphy, W. J. (2001) Transplant. Proc. 33, 1752–1753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

