Deletion of the Parkin coregulated gene causes male sterility in the quaking(viable) mouse mutant
- PMID: 15148410
- PMCID: PMC420406
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0401832101
Deletion of the Parkin coregulated gene causes male sterility in the quaking(viable) mouse mutant
Abstract
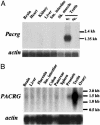
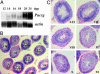
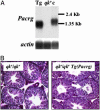
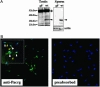
Quaking(viable) (qk(v)) is a recessive neurological mouse mutation with severe dysmyelination of the CNS and spermiogenesis failure. The molecular lesion in the qk(v) mutant is a deletion of approximately 1 Mb on mouse chromosome 17 that alters the expression of the qk gene in oligodendrocytes. Complementation analysis between the qk(v) mutation and qk mutant alleles generated through chemical mutagenesis showed that the male sterility is a distinctive feature of the qk(v) allele. This observation suggested that the sperm differentiation defect in qk(v) is due to the deletion of a gene(s) distinct from qk. Here, we demonstrate that the deletion of Pacrg is the cause of male sterility in the qk(v) mutant. Pacrg is the mouse homologue of the human PARKIN-coregulated gene (PACRG), which encodes for a protein whose biochemical function remains unclear. We show that Pacrg is highly expressed in the testes in both mice and humans. In addition, the expression pattern of Pacrg during spermiogenesis suggests that it plays a role in sperm differentiation. In support of this hypothesis, we show that transgenic expression of Pacrg in testes restores spermiogenesis and fertility in qk(v) males. This finding provides the first in vivo evidence, to our knowledge, for the function of Pacrg in a model organism. Immunolocalization experiments on isolated spermatozoa show that the Pacrg protein is present in mature sperm. Remarkably, the mammalian Pacrg protein shares significant sequence similarities with gene products from flagellated protozoans, suggesting that Pacrg may be necessary for proper flagellar formation in many organisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The neurological mutant quaking(viable) is Parkin deficient.Mamm Genome. 2004 Mar;15(3):210-7. doi: 10.1007/s00335-003-2333-5. Mamm Genome. 2004. PMID: 15014970
-
Deletion of the Parkin co-regulated gene causes defects in ependymal ciliary motility and hydrocephalus in the quakingviable mutant mouse.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Apr 15;19(8):1593-602. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq031. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Hum Mol Genet. 2010. PMID: 20106870
-
Patched1 haploinsufficiency impairs ependymal cilia function of the quaking viable mice, leading to fatal hydrocephalus.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011 Jun;47(2):100-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Apr 5. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21447392
-
Molecular defects in the dysmyelinating mutant quaking.J Neurosci Res. 1998 Feb 15;51(4):417-22. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19980215)51:4<417::AID-JNR1>3.0.CO;2-F. J Neurosci Res. 1998. PMID: 9514195 Review.
-
QUAKING KH domain proteins as regulators of glial cell fate and myelination.RNA Biol. 2005 Apr;2(2):37-40. doi: 10.4161/rna.2.2.1603. Epub 2005 Apr 9. RNA Biol. 2005. PMID: 17132940 Review.
Cited by
-
Disruption of Ttll5/stamp gene (tubulin tyrosine ligase-like protein 5/SRC-1 and TIF2-associated modulatory protein gene) in male mice causes sperm malformation and infertility.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 24;288(21):15167-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.453936. Epub 2013 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23558686 Free PMC article.
-
HAG1 and SWI3A/B control of male germ line development in P. patens suggests conservation of epigenetic reproductive control across land plants.Plant Reprod. 2021 Jun;34(2):149-173. doi: 10.1007/s00497-021-00409-0. Epub 2021 Apr 11. Plant Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33839924 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal Exposure to DEHP Affects Spermatogenesis and Sperm DNA Methylation in a Strain-Dependent Manner.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 5;10(7):e0132136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132136. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26244509 Free PMC article.
-
Rescuing qkV dysmyelination by a single isoform of the selective RNA-binding protein QKI.J Neurosci. 2006 Nov 1;26(44):11278-86. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2677-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17079655 Free PMC article.
-
Mice with alopecia, osteoporosis, and systemic amyloidosis due to mutation in Zdhhc13, a gene coding for palmitoyl acyltransferase.PLoS Genet. 2010 Jun 10;6(6):e1000985. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000985. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20548961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sidman, R. L., Dickie, M. M. & Appel, S. H. (1964) Science 144, 309-311. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, W. I., Gall, A. M., Southard, J. L. & Sidman, R. L. (1971) Biol. Reprod. 5, 30-58. - PubMed
-
- Cox, R. D., Shedlovsky, A., Hamvas, R., Goldsworthy, M., Whittington, J., Connelly, C. S., Dove, W. F. & Lehrach, H. (1994) Genomics 21, 77-84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

