Identification and functional analysis of a defect in the human ALG9 gene: definition of congenital disorder of glycosylation type IL
- PMID: 15148656
- PMCID: PMC1181998
- DOI: 10.1086/422367
Identification and functional analysis of a defect in the human ALG9 gene: definition of congenital disorder of glycosylation type IL
Abstract
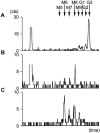
Defects of lipid-linked oligosaccharide assembly lead to alterations of N-linked glycosylation known as "type I congenital disorders of glycosylation" (CDG). Dysfunctions along this stepwise assembly pathway are characterized by intracellular accumulation of intermediate lipid-linked oligosaccharides, the detection of which contributes to the identification of underlying enzymatic defects. Using this approach, we have found, in a patient with CDG, a deficiency of the ALG9 alpha 1,2 mannosyltransferase enzyme, which causes an accumulation of lipid-linked-GlcNAc(2)Man(6) and -GlcNAc(2)Man(8) structures, which was paralleled by the transfer of incomplete oligosaccharides precursors to protein. A homozygous point-mutation 1567G-->A (amino acid substitution E523K) was detected in the ALG9 gene. The functional homology between the human ALG9 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae ALG9, as well as the deleterious effect of the E523K mutation detected in the patient with CDG, were confirmed by a yeast complementation assay lacking the ALG9 gene. The ALG9 defect found in the patient with CDG--who presented with developmental delay, hypotonia, seizures, and hepatomegaly--shows that efficient lipid-linked oligosaccharide synthesis is required for proper human development and physiology. The ALG9 defect presented here defines a novel form of CDG named "CDG-IL."
Figures
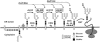

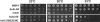
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Entrez, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Entrez/ (for ALG9/DIBD1 cDNA for H. sapiens [accession number AF395532], C. elegans [accession number CAA90107], D. melanogaster [accession number NP_651353], S. pombe [accession number CAB75773], and S. cerevisiae [accession number CAA96122])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for CDG-Ia, ALG9/DIBD1, and BPAD)
References
-
- Baysal BE, Willett-Brozick JE, Badner JA, Corona W, Ferrell RE, Nimgaonkar VL, Detera-Wadleigh SD (2002) A mannosyltransferase gene at 11q23 is disrupted by a translocation breakpoint that co-segregates with bipolar affective disorder in a small family. Neurogenetics 4:43–5310.1007/s10048-001-0129-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Briones P, Vilaseca MA, Schollen E, Ferrer I, Maties M, Busquets C, Artuch R, Gort L, Marco M, van Schaftingen E, Matthijs G, Jaeken J, Chabas A (2002) Biochemical and molecular studies in 26 Spanish patients with congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ia. J Inherit Metab Dis 25:635–64610.1023/A:1022825113506 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burda P, Aebi M (1999) The dolichol pathway of N-linked glycosylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1426:239–257 - PubMed
-
- Burda P, te Heesen S, Brachat A, Wach A, Dusterhoft A, Aebi M (1996) Stepwise assembly of the lipid-linked oligosaccharide in the endoplasmic reticulum of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: identification of the ALG9 gene encoding a putative mannosyl transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7160–716510.1073/pnas.93.14.7160 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

