Linkage disequilibrium mapping via cladistic analysis of single-nucleotide polymorphism haplotypes
- PMID: 15148658
- PMCID: PMC1182006
- DOI: 10.1086/422174
Linkage disequilibrium mapping via cladistic analysis of single-nucleotide polymorphism haplotypes
Abstract
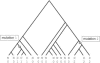
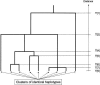
We present a novel approach to disease-gene mapping via cladistic analysis of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) haplotypes obtained from large-scale, population-based association studies, applicable to whole-genome screens, candidate-gene studies, or fine-scale mapping. Clades of haplotypes are tested for association with disease, exploiting the expected similarity of chromosomes with recent shared ancestry in the region flanking the disease gene. The method is developed in a logistic-regression framework and can easily incorporate covariates such as environmental risk factors or additional unlinked loci to allow for population structure. To evaluate the power of this approach to detect disease-marker association, we have developed a simulation algorithm to generate high-density SNP data with short-range linkage disequilibrium based on empirical patterns of haplotype diversity. The results of the simulation study highlight substantial gains in power over single-locus tests for a wide range of disease models, despite overcorrection for multiple testing.
Figures




References
-
- Bertranpetit J, Calafell (1996) Genetic and geographical variability in cystic fibrosis: evolutionary considerations. In: Weiss K (ed) Variation in the human genome. Wiley, Chichester, England, pp 97–114 - PubMed
-
- Everitt BS (1993) Cluster analysis, 3rd edition. Arnold, London, pp 55–89
-
- Gabriel SB, Schaffner SF, Nguyen H, Moore JM, Roy J, Blumenstiel B, Higgins J, DeFelice M, Lochner A, Faggart M, Liu-Cordero SN, Rotimi C, Adeyemo A, Cooper R, Ward R, Lander ES, Daly MJ, Altshuler D (2002) The structure of haplotype blocks in the human genome. Science 296:2225–222910.1126/science.1069424 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

