Total synthesis of TMC-95A and -B via a new reaction leading to Z-enamides. Some preliminary findings as to SAR
- PMID: 15149232
- PMCID: PMC2507741
- DOI: 10.1021/ja049821k
Total synthesis of TMC-95A and -B via a new reaction leading to Z-enamides. Some preliminary findings as to SAR
Abstract
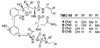
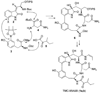
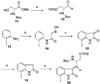
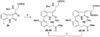
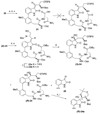
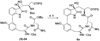
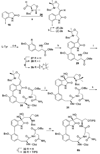
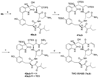
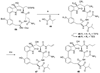
A full account of the total syntheses of proteasome inhibitors TMC-95A and -B is provided. A key feature of the syntheses involved installation of a cis-propenylamide moiety by a thermal rearrangement of an alpha-silylallyl amide. The scope and mechanism of the enamide-forming reaction are discussed. Also provided are some preliminary results from SAR studies. It was found that simplified analogues can retain the full potency of proteasome inhibition.
Figures

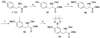


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

