Stress response gene regulation in Chlamydia is dependent on HrcA-CIRCE interactions
- PMID: 15150223
- PMCID: PMC415772
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.11.3384-3391.2004
Stress response gene regulation in Chlamydia is dependent on HrcA-CIRCE interactions
Abstract
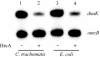
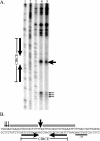
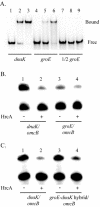
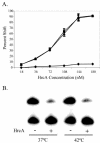
HrcA is a transcriptional repressor that regulates stress response genes in many bacteria by binding to the CIRCE operator. We have previously shown that HrcA regulates the promoter for the dnaK heat shock operon in Chlamydia. Here we demonstrate that HrcA represses a second heat shock promoter that controls the expression of groES and groEL, two other major chlamydial heat shock genes. The CIRCE element of C. trachomatis groEL is the most divergent of known bacterial CIRCE elements, and HrcA had a decreased ability to bind to this nonconsensus operator and repress transcription. We demonstrate that the CIRCE element is necessary and sufficient for transcriptional regulation by chlamydial HrcA and that the inverted repeats of CIRCE are the binding sites for HrcA. Addition of a CIRCE element upstream of a non-heat-shock promoter allowed this promoter to be repressed by HrcA, showing in principle that a chlamydial promoter can be genetically modified to be inducible. These results demonstrate that HrcA is the regulator of the major chlamydial heat shock operons, and we infer that the mechanism of the heat shock response in Chlamydia is derepression. However, derepression is likely to involve more than a direct effect of increased temperature as we found that HrcA binding to CIRCE and HrcA-mediated repression were not altered at temperatures that induce the heat shock response.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The GroE chaperonin machine is a major modulator of the CIRCE heat shock regulon of Bacillus subtilis.EMBO J. 1997 Aug 1;16(15):4579-90. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.15.4579. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9303302 Free PMC article.
-
hrcA, the first gene of the Bacillus subtilis dnaK operon encodes a negative regulator of class I heat shock genes.J Bacteriol. 1996 Feb;178(4):1088-93. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.4.1088-1093.1996. J Bacteriol. 1996. PMID: 8576042 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the heat shock regulator HrcA of Chlamydia trachomatis.J Bacteriol. 2002 Dec;184(23):6566-71. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.23.6566-6571.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12426345 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of the heat shock response in Streptomyces.Arch Microbiol. 2001 Oct;176(4):237-42. doi: 10.1007/s002030100321. Arch Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11685367 Review.
-
Heat-shock and general stress response in Bacillus subtilis.Mol Microbiol. 1996 Feb;19(3):417-28. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.396932.x. Mol Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8830234 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanism of tryptophan-dependent transcriptional regulation in Chlamydia trachomatis.J Bacteriol. 2006 Jun;188(12):4236-43. doi: 10.1128/JB.01660-05. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16740930 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Heat Shock Response in Chlamydia Lacking a Typical Heat Shock Sigma Factor.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 3;12:812448. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.812448. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35046926 Free PMC article.
-
The early gene product EUO is a transcriptional repressor that selectively regulates promoters of Chlamydia late genes.Mol Microbiol. 2012 Jun;84(6):1097-107. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08077.x. Epub 2012 May 25. Mol Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22624851 Free PMC article.
-
The Repressor Function of the Chlamydia Late Regulator EUO Is Enhanced by the Plasmid-Encoded Protein Pgp4.J Bacteriol. 2020 Mar 26;202(8):e00793-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00793-19. Print 2020 Mar 26. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 31988079 Free PMC article.
-
A lineage-specific heat-induced feedback loop controls HrcA to promote chlamydial fitness under stress.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 30:2025.05.30.657042. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.30.657042. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40501649 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Blattner, F. R., G. Plunkett 3rd, C. A. Bloch, N. T. Perna, V. Burland, M. Riley, J. Collado-Vides, J. D. Glasner, C. K. Rode, G. F. Mayhew, J. Gregor, N. W. Davis, H. A. Kirkpatrick, M. A. Goeden, D. J. Rose, B. Mau, and Y. Shao. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453-1474. - PubMed
-
- Brunham, R. C., R. Peeling, I. Maclean, M. L. Kosseim, and M. Paraskevas. 1992. Chlamydia trachomatis-associated ectopic pregnancy: serologic and histologic correlates. J. Infect. Dis. 165:1076-1081. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

