Evidence for an arginine exporter encoded by yggA (argO) that is regulated by the LysR-type transcriptional regulator ArgP in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 15150242
- PMCID: PMC415761
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.11.3539-3546.2004
Evidence for an arginine exporter encoded by yggA (argO) that is regulated by the LysR-type transcriptional regulator ArgP in Escherichia coli
Abstract
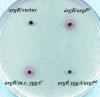
The anonymous open reading frame yggA of Escherichia coli was identified in this study as a gene that is under the transcriptional control of argP (previously called iciA), which encodes a LysR-type transcriptional regulator protein. Strains with null mutations in either yggA or argP were supersensitive to the arginine analog canavanine, and yggA-lac expression in vivo exhibited argP(+)-dependent induction by arginine. Lysine supplementation phenocopied the argP null mutation in that it virtually abolished yggA expression, even in the argP+ strain. The dipeptides arginylalanine and lysylalanine behaved much like arginine and lysine, respectively, to induce and to turn off yggA transcription. Dominant missense mutations in argP (argPd) that conferred canavanine resistance and rendered yggA-lac expression constitutive were obtained. The protein deduced to be encoded by yggA shares similarity with a basic amino acid exporter (LysE) of Corynebacterium glutamicum, and we obtained evidence for increased arginine efflux from E. coli strains with either the argPd mutation or multicopy yggA+. The null yggA mutation abolished the increased arginine efflux from the argPd strain. Our results suggest that yggA encodes an ArgP-regulated arginine exporter, and we have accordingly renamed it argO (for "arginine outward transport"). We propose that the physiological function of argO may be either to prevent the accumulation to toxic levels of canavanine (which is a plant-derived antimetabolite) or arginine or to maintain an appropriate balance between the intracellular lysine and arginine concentrations.
Figures
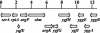
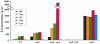
Similar articles
-
Differential protein-DNA contacts for activation and repression by ArgP, a LysR-type (LTTR) transcriptional regulator in Escherichia coli.Microbiol Res. 2018 Jan;206:141-158. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.10.009. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Microbiol Res. 2018. PMID: 29146251
-
Distinct Paths for Basic Amino Acid Export in Escherichia coli: YbjE (LysO) Mediates Export of L-Lysine.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jun 15;197(12):2036-47. doi: 10.1128/JB.02505-14. Epub 2015 Apr 6. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25845847 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional cross-regulation between Gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, demonstrated using ArgP-argO of Escherichia coli and LysG-lysE of Corynebacterium glutamicum.J Bacteriol. 2012 Oct;194(20):5657-66. doi: 10.1128/JB.00947-12. Epub 2012 Aug 17. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22904281 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of arginine biosynthesis, catabolism and transport in Escherichia coli.Amino Acids. 2019 Aug;51(8):1103-1127. doi: 10.1007/s00726-019-02757-8. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Amino Acids. 2019. PMID: 31267155 Review.
-
[Whole genome approach of drug exporter genes and their regulatory networks].Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2003 Nov;58(4):581-94. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 14699850 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
High-yield production of L-serine through a novel identified exporter combined with synthetic pathway in Corynebacterium glutamicum.Microb Cell Fact. 2020 May 29;19(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01374-5. Microb Cell Fact. 2020. PMID: 32471433 Free PMC article.
-
The ArgP protein stimulates the Klebsiella pneumoniae gdhA promoter in a lysine-sensitive manner.J Bacteriol. 2008 Jun;190(12):4351-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00295-08. Epub 2008 Apr 18. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18424527 Free PMC article.
-
LhnR and upstream operon LhnABC in Agrobacterium vitis regulate the induction of tobacco hypersensitive responses, grape necrosis and swarming motility.Mol Plant Pathol. 2012 Sep;13(7):641-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00774.x. Epub 2012 Jan 3. Mol Plant Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22212449 Free PMC article.
-
Derailing the aspartate pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to eradicate persistent infection.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 16;10(1):4215. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12224-3. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31527595 Free PMC article.
-
A high-throughput approach to identify genomic variants of bacterial metabolite producers at the single-cell level.Genome Biol. 2012 May 28;13(5):R40. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-5-r40. Genome Biol. 2012. PMID: 22640862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aleshin, V. V., N. P. Zakataeva, and V. A. Livshits. 1999. A new family of amino-acid-efflux proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24:133-135. - PubMed
-
- Bellmann, A., M. Vrljiæ, M. Patek, H. Sahm, R. Krämer, and L. Eggeling. 2001. Expression control and specificity of the basic amino acid exporter LysE of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microbiology 147:1765-1774. - PubMed
-
- Blattner, F. R., G. Plunkett III, C. A. Bloch, N. T. Perna, V. Burland, M. Riley, J. Collado-Vides, J. D. Glasner, C. K. Rode, G. F. Mayhew, J. Gregor, N. W. Davis, H. A. Kirkpatrick, M. A. Goeden, D. J. Rose, B. Mau, and Y. Shao. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277:1453-1462. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

