DNA repair in higher plants; photoreactivation is the major DNA repair pathway in non-proliferating cells while excision repair (nucleotide excision repair and base excision repair) is active in proliferating cells
- PMID: 15150342
- PMCID: PMC419598
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh591
DNA repair in higher plants; photoreactivation is the major DNA repair pathway in non-proliferating cells while excision repair (nucleotide excision repair and base excision repair) is active in proliferating cells
Abstract
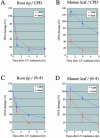
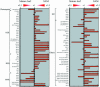
We investigated expression patterns of DNA repair genes such as the CPD photolyase, UV-DDB1, CSB, PCNA, RPA32 and FEN-1 genes by northern hybridization analysis and in situ hybridization using a higher plant, rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. Nipponbare). We found that all the genes tested were expressed in tissues rich in proliferating cells, but only CPD photolyase was expressed in non-proliferating tissue such as the mature leaves and elongation zone of root. The removal of DNA damage, cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers and (6-4) photoproducts, in both mature leaves and the root apical meristem (RAM) was observed after UV irradiation under light. In the dark, DNA damage in mature leaves was not repaired efficiently, but that in the RAM was removed rapidly. Using a rice 22K custom oligo DNA microarray, we compared global gene expression patterns in the shoot apical meristem (SAM) and mature leaves. Most of the excision repair genes were more strongly expressed in SAM. These results suggested that photoreactivation is the major DNA repair pathway for the major UV-induced damage in non-proliferating cells, while both photoreactivation and excision repair are active in proliferating cells.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Plant homologue of flap endonuclease-1: molecular cloning, characterization, and evidence of expression in meristematic tissues.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Feb;42(3):415-27. doi: 10.1023/a:1006349511964. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10798612
-
Rice UV-damaged DNA binding protein homologues are most abundant in proliferating tissues.Gene. 2003 Apr 10;308:79-87. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(03)00447-5. Gene. 2003. PMID: 12711392
-
The photoreactivation of 6 - 4 photoproducts in chloroplast and nuclear DNA depends on the amount of the Arabidopsis UV repair defective 3 protein.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Jul 30;24(1):723. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05439-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39080534 Free PMC article.
-
Repair of UV damage in Halobacterium salinarum.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Jun;31(Pt 3):694-8. doi: 10.1042/bst0310694. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12773185 Review.
-
Nucleosome positioning, nucleotide excision repair and photoreactivation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Dec;36:98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.09.012. Epub 2015 Sep 16. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 26429065 Review.
Cited by
-
Research on plants for the understanding of diseases of nuclear and mitochondrial origin.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:836196. doi: 10.1155/2012/836196. Epub 2012 May 29. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22690124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage and repair.J Nucleic Acids. 2010 Dec 16;2010:592980. doi: 10.4061/2010/592980. J Nucleic Acids. 2010. PMID: 21209706 Free PMC article.
-
Rice exonuclease-1 homologue, OsEXO1, that interacts with DNA polymerase lambda and RPA subunit proteins, is involved in cell proliferation.Plant Mol Biol. 2008 Mar;66(5):519-31. doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9288-6. Epub 2008 Jan 18. Plant Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18231866
-
Regulation and role of Arabidopsis CUL4-DDB1A-DDB2 in maintaining genome integrity upon UV stress.PLoS Genet. 2008 Jun 13;4(6):e1000093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000093. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18551167 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis CRL4 Complexes: Surveying Chromatin States and Gene Expression.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Sep 17;10:1095. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01095. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31608079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ballare C.L., Rousseau,M.C., Searles,P.S., Zaller,J.G., Giordano,C.V., Robson,T.M., Caldwell,M.M., Sala,O.E. and Scopel,A.L. (2001) Impacts of solar ultraviolet-B radiation on terrestrial ecosystems of Tierra del Fuego (southern Argentina). An overview of recent progress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, 62, 67–77. - PubMed
-
- Stapleton A.E., Thornber,C.S. and Walbot,V. (1997) UV-B component of sunlight causes measurable damage in field-grown maize (Zea mays L.): developmental and cellular heterogeneity of damage and repair. Plant Cell Environ., 20, 279–290.
-
- Ries G., Heller,W., Puchta,H., Sandermann,H., Seidlitz,H.K. and Hohn,B. (2000) Elevated UV-B radiation reduces genome stability in plants. Nature, 406, 98–101. - PubMed
-
- Hays J.B. (2002) Arabidopsis thaliana, a versatile model system for study of eukaryotic genome-maintenance functions. DNA Repair, 1, 579–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

