The evolution of a pleiotropic fitness tradeoff in Pseudomonas fluorescens
- PMID: 15150419
- PMCID: PMC419559
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307195101
The evolution of a pleiotropic fitness tradeoff in Pseudomonas fluorescens
Abstract
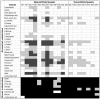
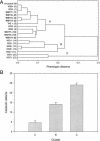
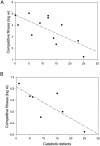
The evolution of ecological specialization is expected to carry a cost, due to either antagonistic pleiotropy or mutation accumulation. In general, it has been difficult to distinguish between these two possibilities. Here, we demonstrate that the experimental evolution of niche-specialist genotypes of the bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens that colonize the air-broth interface of spatially structured microcosms is accompanied by pleiotropic fitness costs in terms of reduced carbon catabolism. Prolonged selection in spatially structured microcosms caused the cost of specialization to decline without loss of the benefits associated with specialization. The decline in the cost of specialization can be explained by either compensatory adaptation within specialist lineages or clonal competition among specialist lineages. These results provide a possible explanation of conflicting accounts for the cost of specialization.
Figures
References
-
- Levene, H. (1953) Am. Nat. 88, 690–692.
-
- Levins, R. (1968) Evolution in Changing Environments (Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton).
-
- Chesson, P. (2000) Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 31, 343–366.
-
- Lynch, M. & Gabriel, W. (1987) Am. Nat. 129, 282–303.
-
- Roughgarden, J. (1972) Am. Nat. 106, 683–718.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

