Role of protein kinase C and NF-kappaB in proteolysis-inducing factor-induced proteasome expression in C(2)C(12) myotubes
- PMID: 15150589
- PMCID: PMC2409757
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601767
Role of protein kinase C and NF-kappaB in proteolysis-inducing factor-induced proteasome expression in C(2)C(12) myotubes
Abstract
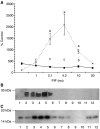
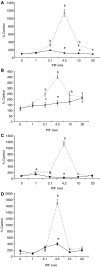
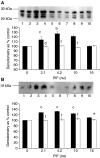
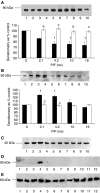
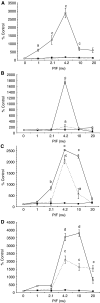
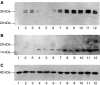
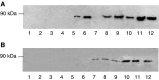
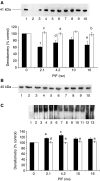
Proteolysis-inducing factor (PIF) is a sulphated glycoprotein produced by cachexia-inducing tumours, which initiates muscle protein degradation through an increased expression of the ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. The role of kinase C (PKC) in PIF-induced proteasome expression has been studied in murine myotubes as a surrogate model of skeletal muscle. Proteasome expression induced by PIF was attenuated by 4alpha-phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (100 nM) and by the PKC inhibitors Ro31-8220 (10 microM), staurosporine (300 nM), calphostin C (300 nM) and Gö 6976 (200 microM). Proteolysis-inducing factor-induced activation of PKC(alpha), with translocation from the cytosol to the membrane at the same concentration as that inducing proteasome expression, and this effect was attenuated by calphostin C. Myotubes transfected with a constitutively active PKC(alpha) (pCO(2)) showed increased expression of proteasome activity, and a longer time course, compared with their wild-type counterparts. In contrast, myotubes transfected with a dominant-negative PKC(alpha) (pKS1), which showed no activation of PKC(alpha) in response to PIF, exhibited no increase in proteasome activity at any time point. Proteolysis-inducing factor-induced proteasome expression has been suggested to involve the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB), which may be activated through PKC. Proteolysis-inducing factor induced a decrease in cytosolic I-kappaBalpha and an increase in nuclear binding of NF-kappaB in pCO(2), but not in pKS1, and the effect in wild-type cells was attenuated by calphostin C, confirming that it was mediated through PKC. This suggests that PKC may be involved in the phosphorylation and degradation of I-kappaBalpha, induced by PIF, necessary for the release of NF-kappaB from its inactive cytosolic complex.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of proteasome expression in skeletal muscle is attenuated by inhibitors of NF-kappaB activation.Br J Cancer. 2004 Nov 1;91(9):1742-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602165. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15477867 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB mediates proteolysis-inducing factor induced protein degradation and expression of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in skeletal muscle.Br J Cancer. 2005 Feb 28;92(4):711-21. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602402. Br J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15714207 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in murine myotubes by proteolysis-inducing factor (PIF) is associated with activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB.Br J Cancer. 2003 Sep 15;89(6):1116-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601132. Br J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12966435 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction pathways involved in proteolysis-inducing factor induced proteasome expression in murine myotubes.Br J Cancer. 2003 Nov 3;89(9):1783-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601328. Br J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 14583784 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway as a therapeutic target for muscle wasting.J Support Oncol. 2005 May-Jun;3(3):209-17. J Support Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15915823 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of proteasome expression in skeletal muscle is attenuated by inhibitors of NF-kappaB activation.Br J Cancer. 2004 Nov 1;91(9):1742-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602165. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15477867 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic cancer cachexia: a review of mechanisms and therapeutics.Front Physiol. 2014 Mar 3;5:88. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00088. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24624094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-kappaB mediates proteolysis-inducing factor induced protein degradation and expression of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in skeletal muscle.Br J Cancer. 2005 Feb 28;92(4):711-21. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602402. Br J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15714207 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 and Haemozoin: Wedding Rings for Human Host and Plasmodium falciparum Parasite in Complicated Malaria.J Trop Med. 2011;2011:628435. doi: 10.1155/2011/628435. Epub 2011 May 26. J Trop Med. 2011. PMID: 21760809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beck SA, Smith KL, Tisdale MJ (1991) Anticachectic and antitumor effect of eicosapentaenoic acid and its effect on protein turnover. Cancer Res 51: 6089–6093 - PubMed
-
- Beltman J, McCormick F, Cook SJ (1996) The selective protein kinase C inhibitor, Ro 31-8220 inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphate-1 (MKP-1) expression, induces c-Jun expression and activates Jun N-terminal kinase. J Biol Chem 43: 27018–27024 - PubMed
-
- Bornancin F, Parker P (1996) Phosphorylation of threonine 638 critically controls dephosphorylation and inactivation of protein kinase C α. Curr Biol 6: 1114–1123 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

