Prognostic significance of nm23-H1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 15150613
- PMCID: PMC2409489
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601808
Prognostic significance of nm23-H1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
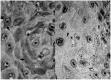
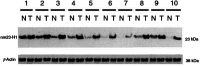
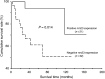
Recent studies indicated nm23-H1 played a role in cancer progression. Therefore, we investigated clinical significance of nm23-H1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). In total, 86 OSCC specimens were immunohistochemically stained with nm23-H1-specific monoclonal antibodies. Immunohistochemical staining of nm23-H1 was confirmed by immunoblotting. The relations between nm23-H1 expression and clinicopathologic variables were evaluated by chi(2) analysis. As increased size of primary tumour could escalate metastatic potential and the data of patients at the late T stage might confound statistical analyses, we thus paid special attention to 54 patients at the early T stage of OSCC. Statistical difference of survival was compared by a log-rank test. Immunohistochemically, nm23-H1 expression was detected in 48.8% (42 out of 86) of tumorous specimens. It positively correlated with larger primary tumour size (P=0.03) and inversely with cigarette-smoking habit (P=0.042). In patients at the early T stage, decreased nm23 expression was associated with increased incidence of lymph node metastasis (P=0.004) and indicated poor survival (P=0.014). Tumour nm23-H1 expression is a prognostic factor for predicting better survival in OSCC patients at the early T stage, which may reflect antimetastatic potential of nm23. Therefore, modulation of nm23-H1 expression in cancer cells can provide a novel possibility of improving therapeutic strategy at this stage. In addition, our results further indicated cigarette smoking could aggravate the extent of nm23-H1 expression and possibly disease progression of OSCC patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The regulation of nm23-H1/NDPK-A in different processes of regional lymph node metastases of oral squamous cell carcinomas].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2003 Aug;21(4):263-6. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14513578 Chinese.
-
Prognostic significance of nm23-H1 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004 Aug;26(2):419-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2004.03.045. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004. PMID: 15296908
-
The NM23 gene and its expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 1999 Jul-Aug;6(4):747-51. doi: 10.3892/or.6.4.747. Oncol Rep. 1999. PMID: 10373649
-
Nm23/NDP kinases in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2006 Aug;38(3-4):169-75. doi: 10.1007/s10863-006-9031-4. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2006. PMID: 16944304 Review.
-
Protein-protein interactions: a mechanism regulating the anti-metastatic properties of Nm23-H1.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;384(4-5):351-62. doi: 10.1007/s00210-011-0646-6. Epub 2011 Jun 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21713383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Value of ezrin, maspin and nm23-H1 protein expressions in predicting outcome of patients with head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma treated with radical radiotherapy.J Clin Pathol. 2007 Feb;60(2):185-9. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2006.036624. Epub 2006 May 12. J Clin Pathol. 2007. PMID: 16698950 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasis suppressor genes at the interface between the environment and tumor cell growth.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011;286:107-80. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385859-7.00003-3. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21199781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NM23-H1 Expression of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Association With the Response to Irradiation.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 30;11:646167. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.646167. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33859945 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasis suppressor genes.Histol Histopathol. 2013 Mar;28(3):285-92. doi: 10.14670/HH-28.285. Histol Histopathol. 2013. PMID: 23348381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metastasis-suppressor genes in clinical practice: lost in translation?Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011 Jun;8(6):333-42. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.65. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21522123 Review.
References
-
- Anneroth G, Batsakis J, Luna M (1987) Review of the literature and a recommended system of malignancy grading in oral squamous cell carcinomas. Scand J Dent Res 95: 229–249 - PubMed
-
- Bashyam MD (2002) Understanding cancer metastasis. Cancer 94: 1821–1829 - PubMed
-
- Bevilacqua G, Sobel ME, Liotta LA, Steeg PS (1989) Association of low nm23 levels in human primary infiltrating ductal breast carcinomas with lymph node involvement and other histopathological indicators of high metastatic potential. Cancer Res 49: 5185–5190 - PubMed
-
- Bundgaard T, Bentzen SM, Wildt J (1994) The prognostic effect of tobacco and alcohol consumption in intra-oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol Eur J Cancer 30B: 323–328 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

