The importance of a critical protonation state and the fate of the catalytic steps in class A beta-lactamases and penicillin-binding proteins
- PMID: 15152012
- PMCID: PMC3371256
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M313143200
The importance of a critical protonation state and the fate of the catalytic steps in class A beta-lactamases and penicillin-binding proteins
Abstract
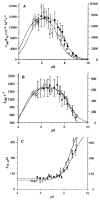
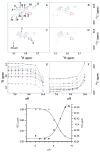
Beta-lactamases and penicillin-binding proteins are bacterial enzymes involved in antibiotic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics and biosynthetic assembly of cell wall, respectively. Members of these large families of enzymes all experience acylation by their respective substrates at an active site serine as the first step in their catalytic activities. A Ser-X-X-Lys sequence motif is seen in all these proteins, and crystal structures demonstrate that the side-chain functions of the serine and lysine are in contact with one another. Three independent methods were used in this report to address the question of the protonation state of this important lysine (Lys-73) in the TEM-1 beta-lactamase from Escherichia coli. These techniques included perturbation of the pK(a) of Lys-73 by the study of the gamma-thialysine-73 variant and the attendant kinetic analyses, investigation of the protonation state by titration of specifically labeled proteins by nuclear magnetic resonance, and by computational treatment using the thermodynamic integration method. All three methods indicated that the pK(a) of Lys-73 of this enzyme is attenuated to 8.0-8.5. It is argued herein that the unique ground-state ion pair of Glu-166 and Lys-73 of class A beta-lactamases has actually raised the pK(a) of the active site lysine to 8.0-8.5 from that of the parental penicillin-binding protein. Whereas we cannot rule out that Glu-166 might activate the active site water, which in turn promotes Ser-70 for the acylation event, such as proposed earlier, we would like to propose as a plausible alternative for the acylation step the possibility that the ion pair would reconfigure to the protonated Glu-166 and unprotonated Lys-73. As such, unprotonated Lys-73 could promote serine for acylation, a process that should be shared among all active-site serine beta-lactamases and penicillin-binding proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
pKa, MM, and QM studies of mechanisms of beta-lactamases and penicillin-binding proteins: acylation step.J Comput Chem. 2002 Dec;23(16):1559-76. doi: 10.1002/jcc.10129. J Comput Chem. 2002. PMID: 12395425
-
Structural aspects for evolution of beta-lactamases from penicillin-binding proteins.J Am Chem Soc. 2003 Aug 13;125(32):9612-8. doi: 10.1021/ja034861u. J Am Chem Soc. 2003. PMID: 12904027
-
The basis for resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics by penicillin-binding protein 2a of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 24;279(39):40802-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403589200. Epub 2004 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15226303
-
Serine beta-lactamases and penicillin-binding proteins.Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:37-67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.000345. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991. PMID: 1741619 Review. No abstract available.
-
Structural and mechanistic aspects of evolution of beta-lactamases and penicillin-binding proteins.Curr Pharm Des. 1999 Nov;5(11):929-37. Curr Pharm Des. 1999. PMID: 10539997 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrolytic mechanism of OXA-58 enzyme, a carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D β-lactamase from Acinetobacter baumannii.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 28;286(43):37292-303. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.280115. Epub 2011 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21880707 Free PMC article.
-
Re-examining the role of Lys67 in class C beta-lactamase catalysis.Protein Sci. 2009 Mar;18(3):662-9. doi: 10.1002/pro.60. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19241376 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into the enzymatic diversity of flavin-trafficking protein (Ftp; formerly ApbE) in flavoprotein biogenesis in the bacterial periplasm.Microbiologyopen. 2016 Feb;5(1):21-38. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.306. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Microbiologyopen. 2016. PMID: 26626129 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of lysine pK values using [5-13C]lysine: application to the lyase domain of DNA Pol beta.J Am Chem Soc. 2006 Jun 28;128(25):8104-5. doi: 10.1021/ja061473u. J Am Chem Soc. 2006. PMID: 16787052 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of a preacylation complex of the β-lactamase inhibitor sulbactam bound to a sulfenamide bond-containing thiol-β-lactamase.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Oct 10;134(40):16798-804. doi: 10.1021/ja3073676. Epub 2012 Sep 26. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22974281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kotra LP, Samama JP, Mobashery S. In: Bacterial Resistance to Antimicrobials, Mechanisms, Genetics, Medical Practice and Public Health. Lewis A, Salyers A, Haber H, Wax RG, editors. Marcel Dekker, Inc; New York: 2002. pp. 123–159.
-
- Bush K, Mobashery S. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1998;456:71–98. - PubMed
-
- Herzberg O, Moult J. Science. 1987;236:694–701. - PubMed
-
- Strynadka NCJ, Adachi H, Jensen SE, Johns K, Sielecki A, Betzel C, Sutoh K, James MNG. Nature. 1992;359:700–705. - PubMed
-
- Maveyraud L, Massova I, Birck C, Miyashita K, Samama JP, Mobashery S. J Am Chem Soc. 1996;118:7435–7440.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

