Independent functions of hsp90 in neurotransmitter release and in the continuous synaptic cycling of AMPA receptors
- PMID: 15152036
- PMCID: PMC6729466
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0594-04.2004
Independent functions of hsp90 in neurotransmitter release and in the continuous synaptic cycling of AMPA receptors
Abstract
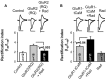
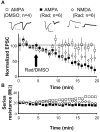
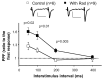
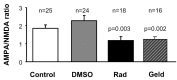
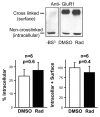
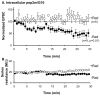
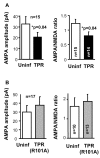
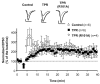
The delivery of neurotransmitter receptors into synapses is essential for synaptic function and plasticity. In particular, AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPA receptors) reach excitatory synapses according to two distinct routes: a regulated pathway, which operates transiently during synaptic plasticity, and a constitutive pathway, which maintains synaptic function under conditions of basal transmission. However, the specific mechanisms that distinguish these two trafficking pathways are essentially unknown. Here, we evaluate the role of the molecular chaperone hsp90 (heat shock protein 90) in excitatory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. On one hand, we found that hsp90 is necessary for the efficient neurotransmitter release at the presynaptic terminal. In addition, we identified hsp90 as a critical component of the cellular machinery that delivers AMPA receptors into the postsynaptic membrane. Using the hsp90-specific inhibitors radicicol and geldanamycin, we show that hsp90 is required for the constitutive trafficking of AMPA receptors into synapses during their continuous cycling between synaptic and nonsynaptic sites. In contrast, hsp90 function is not required for either the surface delivery of AMPA receptors into the nonsynaptic plasma membrane or for the acute, regulated delivery of AMPA receptors into synapses during plasticity induction (long-term potentiation). The synaptic cycling of AMPA receptors was also blocked by an hsp90-binding tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain, suggesting that the role of hsp90 in AMPA receptor trafficking is mediated by a TPR domain-containing protein. These results demonstrate new roles for hsp90 in synaptic function by controlling neurotransmitter release and, independently, by mediating the continuous cycling of synaptic AMPA receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subunit-specific rules governing AMPA receptor trafficking to synapses in hippocampal pyramidal neurons.Cell. 2001 May 4;105(3):331-43. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00321-x. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11348590
-
Postsynaptic density 95 controls AMPA receptor incorporation during long-term potentiation and experience-driven synaptic plasticity.J Neurosci. 2004 Jan 28;24(4):916-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4733-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14749436 Free PMC article.
-
PIP3 controls synaptic function by maintaining AMPA receptor clustering at the postsynaptic membrane.Nat Neurosci. 2010 Jan;13(1):36-44. doi: 10.1038/nn.2462. Epub 2009 Dec 13. Nat Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20010819 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of postsynaptic localization of AMPA-type glutamate receptors and their regulation during long-term potentiation.Sci Signal. 2019 Jan 1;12(562):eaar6889. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aar6889. Sci Signal. 2019. PMID: 30600260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of AMPA receptors and synaptic plasticity.Neuroscience. 2009 Jan 12;158(1):105-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.02.037. Epub 2008 Feb 29. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18424006 Review.
Cited by
-
The mechanism of acetylcholine receptor in binding MuSK in myasthenia gravis and the role of HSP90 molecular chaperone.Am J Transl Res. 2016 Apr 15;8(4):1763-8. eCollection 2016. Am J Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27186300 Free PMC article.
-
Localized molecular chaperone synthesis maintains neuronal dendrite proteostasis.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 30;15(1):10796. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55055-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39737952 Free PMC article.
-
HSP90 is a chaperone for DLK and is required for axon injury signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 16;115(42):E9899-E9908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1805351115. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30275300 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic morphine alters the presynaptic protein profile: identification of novel molecular targets using proteomics and network analysis.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25535. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025535. Epub 2011 Oct 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22043286 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathway adaptations and novel protein kinase A substrates related to behavioral sensitization to cocaine.J Neurochem. 2009 Jul;110(1):363-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06140.x. Epub 2009 May 3. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19457111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Archibald K, Perry MJ, Molnar E, Henley JM (1998) Surface expression and metabolic half-life of AMPA receptors in cultured rat cerebellar granule cells. Neuropharmacology 37: 1345–1353. - PubMed
-
- Barral JM, Hutagalung AH, Brinker A, Hartl FU, Epstein HF (2002) Role of the myosin assembly protein UNC-45 as a molecular chaperone for myosin. Science 295: 669–671. - PubMed
-
- Barry MF, Ziff EB (2002) Receptor trafficking and the plasticity of excitatory synapses. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12: 279–286. - PubMed
-
- Blatch GL, Lassle M (1999) The tetratricopeptide repeat: a structural motif mediating protein-protein interactions. BioEssays 21: 932–939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
