Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase activation is required for metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression in hippocampal area CA1
- PMID: 15152046
- PMCID: PMC6729463
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5407-03.2004
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase activation is required for metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression in hippocampal area CA1
Abstract
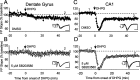
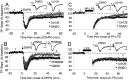
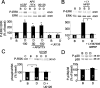
Activation of group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) induces long-term depression (LTD) of synaptic transmission that relies on dendritic protein synthesis. We investigated the signal transduction pathways required for mGluR-LTD to identify candidate mechanisms for mGluR regulation of synaptic protein synthesis. Our results demonstrate a role for extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK), a subclass of the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), in mGluR-LTD in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus. Inhibitors of the upstream kinase of ERK, MAP/ERK kinase significantly reduce mGluR-LTD induced by the group 1 agonist dihydroxyphenylglycine (DHPG) and synaptic stimulation but do not affect NMDA receptor-dependent LTD. In contrast, inhibitors of p38 MAPK were ineffective against DHPG-induced LTD. Consistent with the role of ERK in mGluR-LTD, we observed that DHPG treatment of hippocampal slices (isolated CA1), at concentrations that induce LTD, results in a robust phosphorylation of ERK but not of p38 MAPK. These results point to ERK as an important regulator of mGluR-LTD and a potential mechanism for mGluR regulation of synaptic protein synthesis.
Figures
References
-
- Ahn S, Ginty DD, Linden DJ (1999) A late phase of cerebellar long-term depression requires activation of CaMKIV and CREB. Neuron 23: 559–568. - PubMed
-
- Bolshakov VY, Carboni L, Cobb MH, Siegelbaum SA, Belardetti F (2000) Dual MAP kinase pathways mediate opposing forms of long-term plasticity at CA3-CA1 synapses. Nat Neurosci 3: 1107–1112. - PubMed
-
- Coogan AN, O'Leary DM, O'Connor JJ (1999) P42/44 MAP kinase inhibitor PD98059 attenuates multiple forms of synaptic plasticity in rat dentate gyrus in vitro. J Neurophysiol 81: 103–110. - PubMed
-
- Ferraguti F, Baldani-Guerra B, Corsi M, Nakanishi S, Corti C (1999) Activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 by metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur J Neurosci 11: 2073–2082. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
