Reduced progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice treated with lacidipine is associated with a decreased susceptibility of low-density lipoprotein to oxidation
- PMID: 15154916
- PMCID: PMC2517459
- DOI: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2004.00375.x
Reduced progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice treated with lacidipine is associated with a decreased susceptibility of low-density lipoprotein to oxidation
Abstract
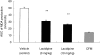
A study has been carried out in the apolipoprotein (apo) E-deficient mouse to investigate the activity of lacidipine (a calcium antagonist with antioxidant properties) in inhibiting the development of atherosclerotic lesions; of particular interest were changes in the susceptibility of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) to oxidation. Mice receiving a Western-type diet to accelerate the development of atherosclerosis were treated orally with vehicle or lacidipine at 3 or 10 mg/kg/day for 8 weeks. Lacidipine treatment (at 3 or 10 mg/kg) had no effect on the plasma lipid profile. However, a significant (P < 0.01) dose-related reduction of 43 and 50% of the aortic lesion area in respect to vehicle-treated mice was observed. Moreover, the resistance of mouse plasma LDL to undergo lipid peroxidation was significantly (P < 0.01) increased in apo E-deficient mice treated with lacidipine. The native LDL-like particle, derived from apo E-deficient mice treated with lacidipine, contained significantly lower concentrations of malonyldialdehyde than the vehicle-treated control group (P < 0.01). After exposure to human umbilical vein endothelial cells, LDL-like particle vitamin E levels (expressed as area under the curve; AUC), were significantly higher (P < 0.01) in both the 3 and 10 mg/kg lacidipine-treated groups, in comparison with the vehicle-treated control animals. We conclude that lacidipine reduced the extent of the atherosclerotic area in hypercholesterolaemic apo E-deficient mice, and that this reduction may be associated with the capacity of the drug to decrease the susceptibility of LDL to oxidation.
Figures






References
-
- van Amsterdam FTM, Roveri A, Maiorino M, Ratti E, Ursini F. Lacidipine: a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist with antioxidant activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1992;12:183–187. - PubMed
-
- Avogaro P, Bittolo Bon G, Cazzolato G. Presence of a modified low density lipoprotein in humans. Atherosclerosis. 1988;8,:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Babiy AV, Gebicky JM, Sullivan DR. Increased oxidazibility of plasma lipoproteins in diabetic patients can be decreased by probucol therapy and is not due to glycation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992;43:995–1000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

