tcaA inactivation increases glycopeptide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 15155184
- PMCID: PMC415614
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.6.1953-1959.2004
tcaA inactivation increases glycopeptide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
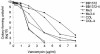
The experimental deletion of the tcaRAB region has been shown to increase teicoplanin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. By sequential genetic complementation of a tcaRAB mutant, we identified tcaA as the key gene within tcaRAB that is responsible for changes in glycopeptide resistance levels. Northern blot analysis of the tcaRAB region showed that the tcaA gene is expressed only weakly over the growth cycle and is strongly inducible by teicoplanin. Among some clinical isolates tested, glycopeptide-intermediate-resistant (GISA) strains Michigan and SA137/93G were found to have truncated tcaA genes. While the former carries a nucleotide insertion that creates a premature stop codon, the latter was found to harbor an IS256 insertion. Complementation of these two GISA strains with a functional tcaA allele reduced their levels of teicoplanin and vancomycin resistance five- to eightfold and twofold, respectively. The data presented here indicate that inactivation of tcaA contributes to and plays a relevant role in glycopeptide resistance in S. aureus clinical isolates.
Figures

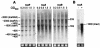

Similar articles
-
Functional characterization of TcaA: minimal requirement for teicoplanin susceptibility and role in Caenorhabditis elegans virulence.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Nov;51(11):3836-43. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00722-07. Epub 2007 Aug 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17709474 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of a novel three-cistronic operon tcaR-tcaA-tcaB increases teicoplanin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Oct 18;1523(2-3):135-9. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(00)00133-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 11042376
-
Comparative analysis and validation of different assays for glycopeptide susceptibility among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains.J Microbiol Methods. 2004 May;57(2):231-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2004.01.012. J Microbiol Methods. 2004. PMID: 15063063
-
Glycopeptide resistant Staphylococcus.J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2004 Oct-Nov;51(8-9):370-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.2004.00774.x. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2004. PMID: 15525368 Review.
-
Structure and mechanism of action of teicoplanin.J Hosp Infect. 1986 Mar;7 Suppl A:79-83. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(86)90011-3. J Hosp Infect. 1986. PMID: 2871101 Review.
Cited by
-
Draft Genome Sequences of Three Northern German Epidemic Staphylococcus aureus (ST247) Strains Containing Multiple Copies of IS256.Genome Announc. 2016 Sep 8;4(5):e00936-16. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00936-16. Genome Announc. 2016. PMID: 27609917 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of genes of the cell wall stimulon in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus exhibiting vancomycin-intermediate- S. aureus-type resistance to vancomycin.J Bacteriol. 2006 Feb;188(3):1120-33. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.3.1120-1133.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16428416 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Extracellular Vesicles Elicit an Immunostimulatory Response in vivo on the Murine Mammary Gland.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Aug 22;8:277. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00277. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30186772 Free PMC article.
-
DNA microarray-based identification of genes associated with glycopeptide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 Aug;49(8):3404-13. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.8.3404-3413.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16048954 Free PMC article.
-
walK and clpP mutations confer reduced vancomycin susceptibility in Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Aug;55(8):3870-81. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01563-10. Epub 2011 May 31. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21628539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ariza, J., M. Pujol, J. Cabo, C. Pena, N. Fernandez, J. Linares, J. Ayats, and F. Gudiol. 1999. Vancomycin in surgical infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with heterogeneous resistance to vancomycin. Lancet 353:1587-1588. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff, M., M. Roos, J. Putnik, A. Wada, P. Glanzmann, P. Giachino, P. Vaudaux, and B. Berger-Bächi. 2001. Involvement of multiple genetic loci in Staphylococcus aureus teicoplanin resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 194:77-82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

