Fitness cost of SCCmec and methicillin resistance levels in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 15155238
- PMCID: PMC415608
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.6.2295-2297.2004
Fitness cost of SCCmec and methicillin resistance levels in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
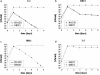
Transformation of a type I SCCmec element into Staphylococcus aureus yielded highly oxacillin-resistant transformants with a reduced growth rate. Faster-growing variants could again be selected at the cost of reduced resistance levels, demonstrating an inverse correlation between oxacillin resistance levels and growth rate.
Figures
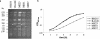

Similar articles
-
Epidemiologic distribution of the arginine catabolic mobile element among selected methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus isolates.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Jun;45(6):1981-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00273-07. Epub 2007 Apr 4. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17409207 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary relationships between sporadic and epidemic strains of healthcare-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008 Jul;14(7):659-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2008.02015.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008. PMID: 18558938
-
Unusual form of oxacillin resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical strains.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008 Aug;61(4):387-95. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2008.04.003. Epub 2008 May 27. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18508224
-
The molecular evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007 Mar;13(3):222-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01573.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007. PMID: 17391376 Review.
-
The evolution of Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Genet Evol. 2008 Dec;8(6):747-63. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2008.07.007. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Infect Genet Evol. 2008. PMID: 18718557 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene acquisition at the insertion site for SCCmec, the genomic island conferring methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2008 Feb;190(4):1276-83. doi: 10.1128/JB.01128-07. Epub 2007 Dec 14. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18083809 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Vesicles Are the Dominant Structural Components of Ceftazidime-Induced Biofilm Formation in an Oxacillin-Sensitive MRSA.Front Microbiol. 2019 Mar 21;10:571. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00571. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30949156 Free PMC article.
-
Fitness of Streptococcus pneumoniae fluoroquinolone-resistant strains with topoisomerase IV recombinant genes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Mar;52(3):822-30. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00731-07. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18160515 Free PMC article.
-
Nonoptimal DNA topoisomerases allow maintenance of supercoiling levels and improve fitness of Streptococcus pneumoniae.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Mar;55(3):1097-105. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00783-10. Epub 2010 Dec 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21173181 Free PMC article.
-
Tedizolid-Rifampicin Combination Prevents Rifampicin-Resistance on in vitro Model of Staphylococcus aureus Mature Biofilm.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 28;11:2085. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.02085. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32983061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson, D. I., and R. Levin. 1999. The biological cost of antibiotic resistance. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2:489-493. - PubMed
-
- Berger-Bächi, B., and M. L. Kohler. 1983. A novel site on the chromosome of Staphylococcus aureus influencing the level of methicillin resistance: genetic mapping. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 20:305-309.
-
- Figueiredo, A. M., E. Ha, B. N. Kreiswirth, H. de Lencastre, G. J. Noel, L. Senterfit, and A. Tomasz. 1991. In vivo stability of heterogeneous expression classes in clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant staphylococci. J. Infect. Dis. 164:883-887. - PubMed
-
- Ito, T., Y. Katayama, K. Asada, N. Mori, K. Tsutsumimoto, C. Tiensasitorn, and K. Hiramatsu. 2001. Structural comparison of the three types of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec integrated in the chromosome in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45:1323-1336. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

